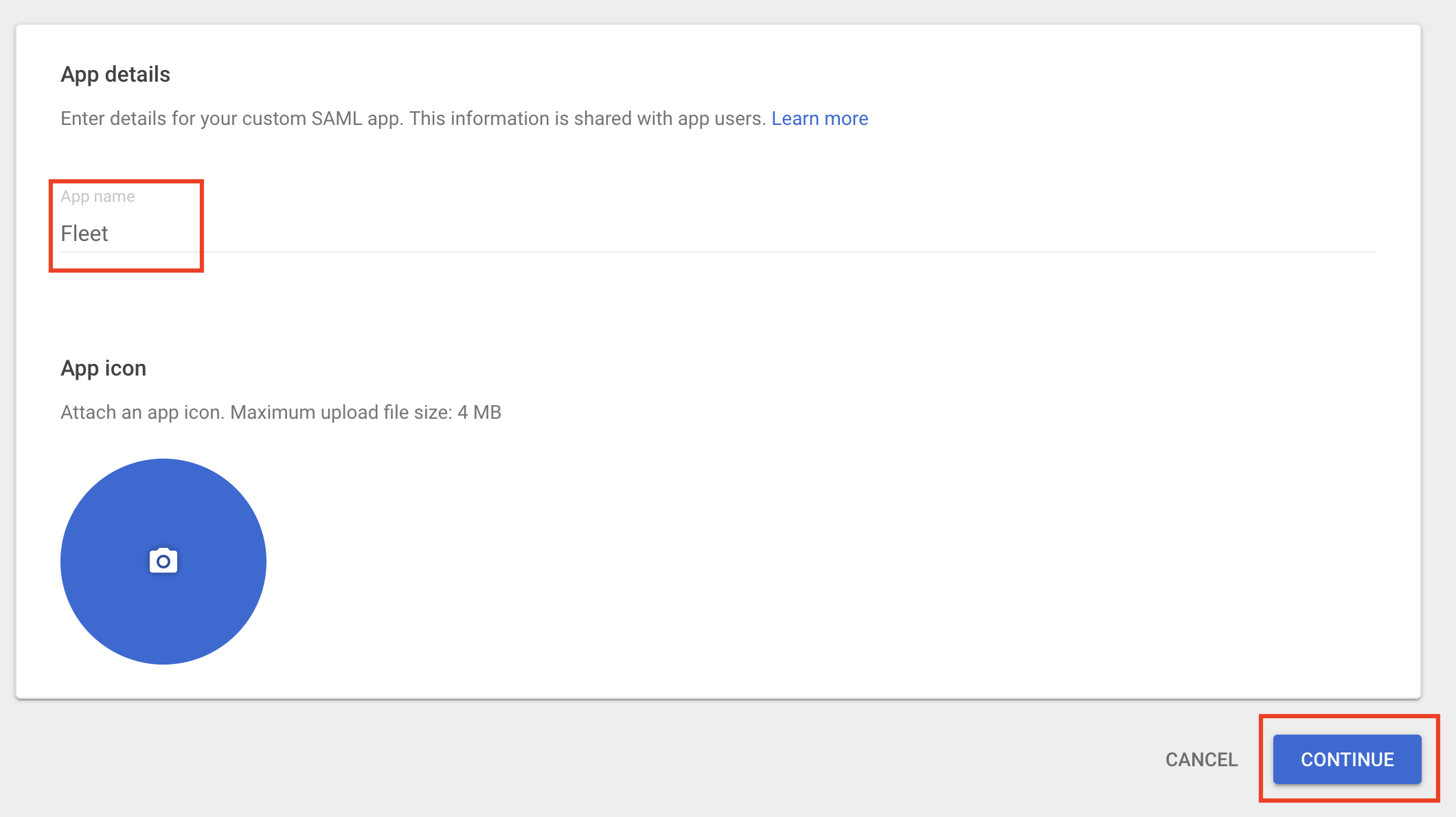
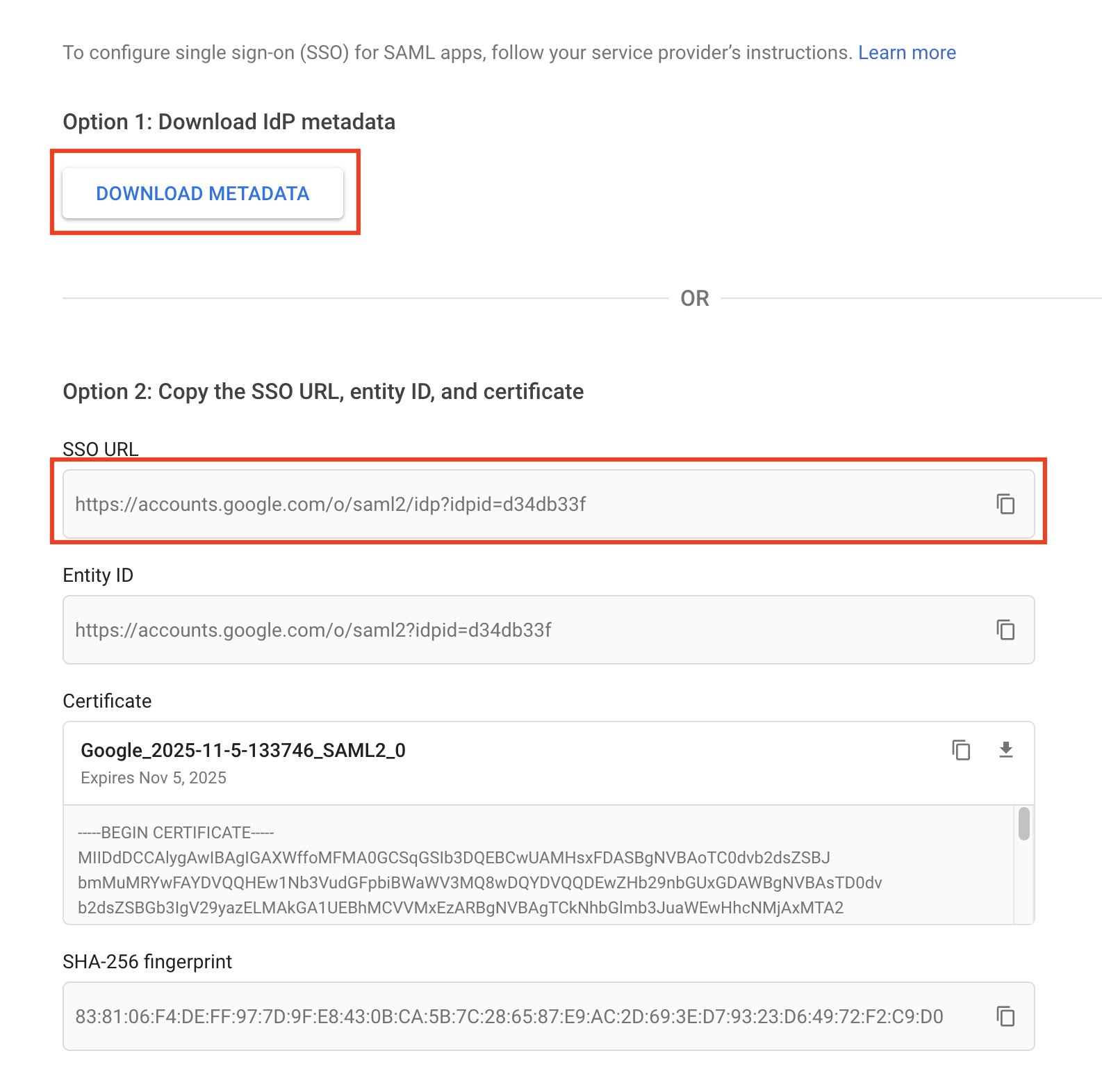
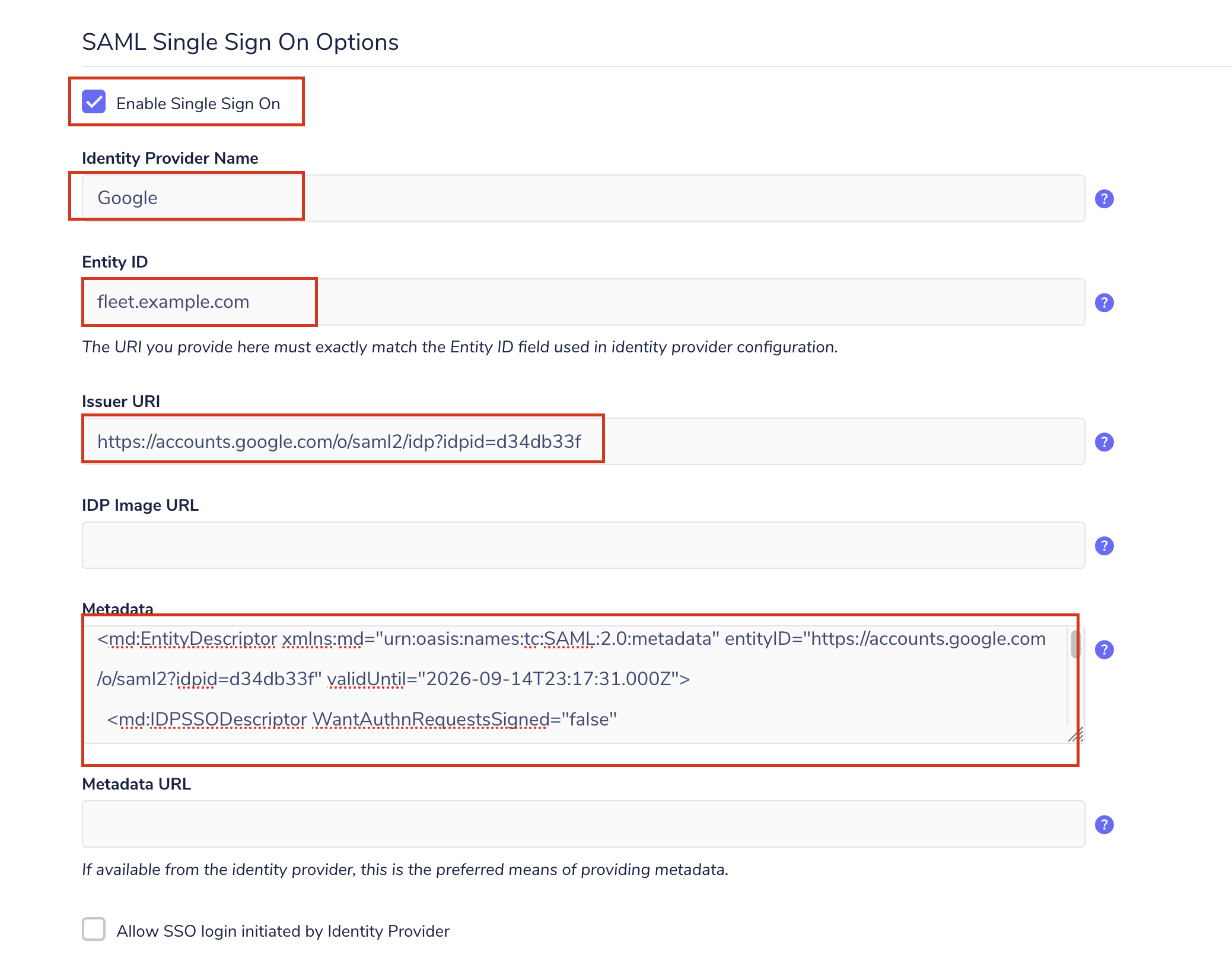
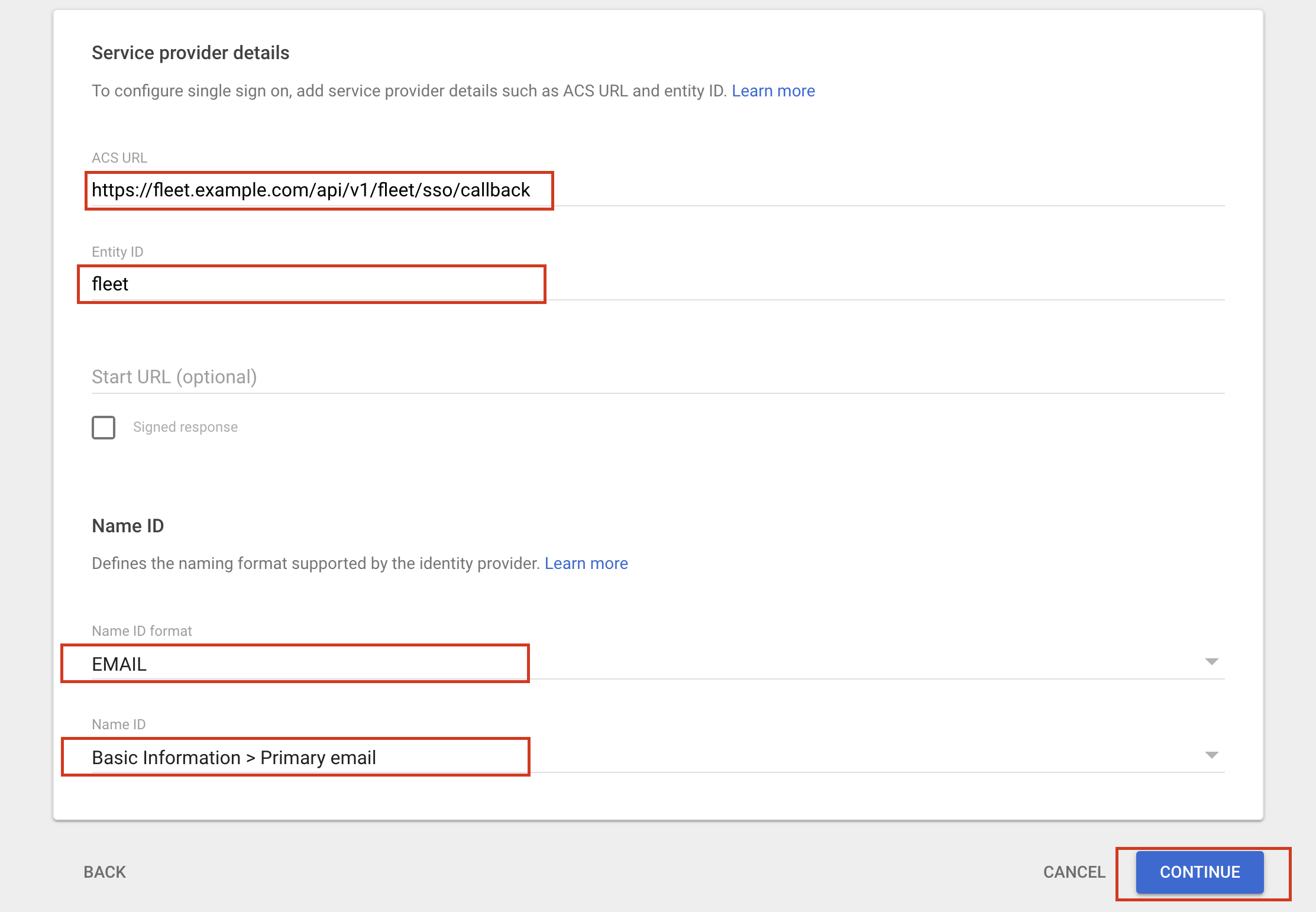
# Checklist for submitter If some of the following don't apply, delete the relevant line. - [X] Changes file added for user-visible changes in `changes/` or `orbit/changes/`. See [Changes files](https://fleetdm.com/docs/contributing/committing-changes#changes-files) for more information. - [X] Documented any API changes (docs/Using-Fleet/REST-API.md or docs/Contributing/API-for-contributors.md) closes https://github.com/fleetdm/fleet/issues/10778 --------- Co-authored-by: Martin Angers <martin.n.angers@gmail.com>
99 KiB
Configuration
Configuring the Fleet binary
For information on how to run the fleet binary, find detailed usage information by running fleet --help. This document is a more detailed version of the data presented in the help output text. If you prefer to use a CLI instead of a web browser, we hope you like the binary interface of the Fleet application!
High-level configuration overview
In order to get the most out of running the Fleet server, it is helpful to establish a mutual understanding of what the desired architecture looks like and what it's trying to accomplish.
Your Fleet server's two main purposes are:
- To serve as your osquery TLS server
- To serve the Fleet web UI, which allows you to manage osquery configuration, query hosts, etc.
The Fleet server allows you to persist configuration, manage users, etc. Thus, it needs a database. Fleet uses MySQL and requires you to supply configurations to connect to a MySQL server. It is also possible to configure your connection to a MySQL replica in addition to the primary. This is for reading only. Fleet also uses Redis to perform more high-speed data access action throughout the applications lifecycle (for example, distributed query result ingestion). Thus, Fleet also requires that you supply Redis connection configurations.
Fleet can scale to hundreds of thousands of devices with a single Redis instance and is also compatible with Redis Cluster. Fleet does not support Redis Sentinel.
Since Fleet is a web application, when you run it there are other configurations that must be defined, such as:
- The TLS certificates that Fleet should use to terminate TLS.
When deploying Fleet, mitigate DoS attacks as you would when deploying any app.
Since Fleet is an osquery TLS server, you are also able to define configurations that can customize your experience there, such as:
- The destination of the osquery status and result logs on the local filesystem
- Various details about the refresh/check-in intervals for your hosts
Commands
The fleet binary contains several "commands." Similarly to how git has many commands (git status, git commit, etc.), the fleet binary accepts the following commands:
fleet prepare dbfleet servefleet versionfleet config_dump
Options
How do you specify options?
You can specify options in the order of precedence via
- a configuration file (in YAML format)
- environment variables
- command-line flags
For example, all of the following ways of launching Fleet are equivalent:
1. Using a YAML config file
echo '
mysql:
address: 127.0.0.1:3306
database: fleet
username: root
password: toor
redis:
address: 127.0.0.1:6379
server:
cert: /tmp/server.cert
key: /tmp/server.key
logging:
json: true
' > /tmp/fleet.yml
fleet serve --config /tmp/fleet.yml
For more information on using YAML configuration files with fleet, please see the configuration files documentation.
2. Using only environment variables
FLEET_MYSQL_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:3306 \
FLEET_MYSQL_DATABASE=fleet \
FLEET_MYSQL_USERNAME=root \
FLEET_MYSQL_PASSWORD=toor \
FLEET_REDIS_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:6379 \
FLEET_SERVER_CERT=/tmp/server.cert \
FLEET_SERVER_KEY=/tmp/server.key \
FLEET_LOGGING_JSON=true \
/usr/bin/fleet serve
3. Using only CLI flags
/usr/bin/fleet serve \
--mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 \
--mysql_database=fleet \
--mysql_username=root \
--mysql_password=toor \
--redis_address=127.0.0.1:6379 \
--server_cert=/tmp/server.cert \
--server_key=/tmp/server.key \
--logging_json
What are the options?
Note that all option names can be converted consistently from flag name to environment variable and visa-versa. For example, the --mysql_address flag would be the FLEET_MYSQL_ADDRESS. Further, specifying the mysql_address option in the config would follow the pattern:
mysql:
address: 127.0.0.1:3306
And mysql_read_replica_address would be:
mysql_read_replica:
address: 127.0.0.1:3307
Basically, just capitalize the option and prepend FLEET_ to it to get the environment variable. The conversion works the same the opposite way.
All duration-based settings accept valid time units of s, m, h.
MySQL
This section describes the configuration options for the primary. Suppose you also want to set up a read replica. In that case the options are the same, except that the YAML section is mysql_read_replica, and the flags have the mysql_read_replica_ prefix instead of mysql_ (the corresponding environment variables follow the same transformation). Note that there is no default value for mysql_read_replica_address, it must be set explicitly for Fleet to use a read replica, and it is recommended in that case to set a non-zero value for mysql_read_replica_conn_max_lifetime as in some environments, the replica's address may dynamically change to point
from the primary to an actual distinct replica based on auto-scaling options, so existing idle connections need to be recycled
periodically.
mysql_address
For the address of the MySQL server that Fleet should connect to, include the hostname and port.
- Default value:
localhost:3306 - Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_ADDRESS - Config file format:
mysql: address: localhost:3306
mysql_database
This is the name of the MySQL database which Fleet will use.
- Default value:
fleet - Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_DATABASE - Config file format:
mysql: database: fleet
mysql_username
The username to use when connecting to the MySQL instance.
- Default value:
fleet - Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_USERNAME - Config file format:
mysql: username: fleet
mysql_password
The password to use when connecting to the MySQL instance.
- Default value:
fleet - Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_PASSWORD - Config file format:
mysql: password: fleet
mysql_password_path
File path to a file that contains the password to use when connecting to the MySQL instance.
- Default value:
"" - Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_PASSWORD_PATH - Config file format:
mysql: password_path: '/run/secrets/fleetdm-mysql-password'
mysql_tls_ca
The path to a PEM encoded certificate of MYSQL's CA for client certificate authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_TLS_CA - Config file format:
mysql: tls_ca: /path/to/server-ca.pem
mysql_tls_cert
The path to a PEM encoded certificate is used for TLS authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_TLS_CERT - Config file format:
mysql: tls_cert: /path/to/certificate.pem
mysql_tls_key
The path to a PEM encoded private key used for TLS authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_TLS_KEY - Config file format:
mysql: tls_key: /path/to/key.pem
mysql_tls_config
The TLS value in an MYSQL DSN. Can be true,false,skip-verify, or the CN value of the certificate.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_TLS_CONFIG - Config file format:
mysql: tls_config: true
mysql_tls_server_name
This is the server name or IP address used by the client certificate.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_TLS_SERVER_NAME - Config file format:
mysql: server_name: 127.0.0.1
mysql_max_open_conns
The maximum open connections to the database.
- Default value: 50
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_MAX_OPEN_CONNS - Config file format:
mysql: max_open_conns: 50
mysql_max_idle_conns
The maximum idle connections to the database. This value should be equal to or less than mysql_max_open_conns.
- Default value: 50
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_MAX_IDLE_CONNS - Config file format:
mysql: max_idle_conns: 50
mysql_conn_max_lifetime
The maximum amount of time, in seconds, a connection may be reused.
- Default value: 0 (Unlimited)
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_CONN_MAX_LIFETIME - Config file format:
mysql: conn_max_lifetime: 50
mysql_sql_mode
Sets the connection sql_mode. See MySQL Reference for more details.
This setting should not usually be used.
- Default value:
"" - Environment variable:
FLEET_MYSQL_SQL_MODE - Config file format:
mysql: sql_mode: ANSI
Example YAML
mysql:
address: localhost:3306
database: fleet
password: fleet
max_open_conns: 50
max_idle_conns: 50
conn_max_lifetime: 50
Redis
Note that to test a TLS connection to a Redis instance, run the
tlsconnect Go program in tools/redis-tests, e.g., from the root of the repository:
$ go run ./tools/redis-tests/tlsconnect.go -addr <redis_address> -cacert <redis_tls_ca> -cert <redis_tls_cert> -key <redis_tls_key>
# run `go run ./tools/redis-tests/tlsconnect.go -h` for the full list of supported flags
By default, this will set up a Redis pool for that configuration and execute a
PING command with a TLS connection, printing any error it encounters.
redis_address
For the address of the Redis server that Fleet should connect to, include the hostname and port.
- Default value:
localhost:6379 - Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_ADDRESS - Config file format:
redis: address: 127.0.0.1:7369
redis_username
The username to use when connecting to the Redis instance.
- Default value:
<empty> - Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_USERNAME - Config file format:
redis: username: foobar
redis_password
The password to use when connecting to the Redis instance.
- Default value:
<empty> - Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_PASSWORD - Config file format:
redis: password: foobar
redis_database
The database to use when connecting to the Redis instance.
- Default value:
0 - Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_DATABASE - Config file format:
redis: database: 14
redis_use_tls
Use a TLS connection to the Redis server.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_USE_TLS - Config file format:
redis: use_tls: true
redis_duplicate_results
Whether or not to duplicate Live Query results to another Redis channel named LQDuplicate. This is useful in a scenario involving shipping the Live Query results outside of Fleet, near real-time.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_DUPLICATE_RESULTS - Config file format:
redis: duplicate_results: true
redis_connect_timeout
Timeout for redis connection.
- Default value: 5s
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_CONNECT_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
redis: connect_timeout: 10s
redis_keep_alive
The interval between keep-alive probes.
- Default value: 10s
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_KEEP_ALIVE - Config file format:
redis: keep_alive: 30s
redis_connect_retry_attempts
The maximum number of attempts to retry a failed connection to a Redis node. Only certain types of errors are retried, such as connection timeouts.
- Default value: 0 (no retry)
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_CONNECT_RETRY_ATTEMPTS - Config file format:
redis: connect_retry_attempts: 2
redis_cluster_follow_redirections
Whether or not to automatically follow redirection errors received from the Redis server. Applies only to Redis Cluster setups, ignored in standalone Redis. In Redis Cluster, keys can be moved around to different nodes when the cluster is unstable and reorganizing the data. With this configuration option set to true, those (typically short and transient) redirection errors can be handled transparently instead of ending in an error.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_CLUSTER_FOLLOW_REDIRECTIONS - Config file format:
redis: cluster_follow_redirections: true
redis_cluster_read_from_replica
Whether or not to prefer reading from a replica when possible. Applies only to Redis Cluster setups, ignored in standalone Redis.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_CLUSTER_READ_FROM_REPLICA - Config file format:
redis: cluster_read_from_replica: true
redis_tls_cert
This is the path to a PEM-encoded certificate used for TLS authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_TLS_CERT - Config file format:
redis: tls_cert: /path/to/certificate.pem
redis_tls_key
This is the path to a PEM-encoded private key used for TLS authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_TLS_KEY - Config file format:
redis: tls_key: /path/to/key.pem
redis_tls_ca
This is the path to a PEM-encoded certificate of Redis' CA for client certificate authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_TLS_CA - Config file format:
redis: tls_ca: /path/to/server-ca.pem
redis_tls_server_name
The server name or IP address used by the client certificate.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_TLS_SERVER_NAME - Config file format:
redis: tls_server_name: 127.0.0.1
redis_tls_handshake_timeout
The timeout for the Redis TLS handshake part of the connection. A value of 0 means no timeout.
- Default value: 10s
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_TLS_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
redis: tls_handshake_timeout: 10s
redis_max_idle_conns
The maximum idle connections to Redis. This value should be equal to or less than redis_max_open_conns.
- Default value: 3
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_MAX_IDLE_CONNS - Config file format:
redis: max_idle_conns: 50
redis_max_open_conns
The maximum open connections to Redis. A value of 0 means no limit.
- Default value: 0
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_MAX_OPEN_CONNS - Config file format:
redis: max_open_conns: 100
redis_conn_max_lifetime
The maximum time a Redis connection may be reused. A value of 0 means no limit.
- Default value: 0 (Unlimited)
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_CONN_MAX_LIFETIME - Config file format:
redis: conn_max_lifetime: 30m
redis_idle_timeout
The maximum time a Redis connection may stay idle. A value of 0 means no limit.
- Default value: 240s
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_IDLE_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
redis: idle_timeout: 5m
redis_conn_wait_timeout
The maximum time to wait for a Redis connection if the max_open_conns limit is reached. A value of 0 means no wait. This is ignored if Redis is not running in cluster mode.
- Default value: 0
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_CONN_WAIT_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
redis: conn_wait_timeout: 1s
redis_read_timeout
The maximum time to wait to receive a response from a Redis server. A value of 0 means no timeout.
- Default value: 10s
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_READ_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
redis: read_timeout: 5s
redis_write_timeout
The maximum time to wait to send a command to a Redis server. A value of 0 means no timeout.
- Default value: 10s
- Environment variable:
FLEET_REDIS_WRITE_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
redis: write_timeout: 5s
Example YAML
redis:
address: localhost:7369
password: foobar
database: 14
connect_timeout: 10s
connect_retry_attempts: 2
Server
server_address
The address to serve the Fleet webserver.
- Default value:
0.0.0.0:8080 - Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_ADDRESS - Config file format:
server: address: 0.0.0.0:443
server_cert
The TLS cert to use when terminating TLS.
See TLS certificate considerations for more information about certificates and Fleet.
- Default value:
./tools/osquery/fleet.crt - Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_CERT - Config file format:
server: cert: /tmp/fleet.crt
server_key
The TLS key to use when terminating TLS.
- Default value:
./tools/osquery/fleet.key - Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_KEY - Config file format:
server: key: /tmp/fleet.key
server_tls
Whether or not the server should be served over TLS.
- Default value:
true - Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_TLS - Config file format:
server: tls: false
server_tls_compatibility
Configures the TLS settings for compatibility with various user agents. Options are modern and intermediate. These correspond to the compatibility levels defined by the Mozilla OpSec team (updated July 24, 2020).
- Default value:
intermediate - Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_TLS_COMPATIBILITY - Config file format:
server: tls_compatibility: intermediate
server_url_prefix
Sets a URL prefix to use when serving the Fleet API and frontend. Prefixes should be in the form /apps/fleet (no trailing slash).
Note that some other configurations may need to be changed when modifying the URL prefix. In particular, URLs that are provided to osquery via flagfile, the configuration served by Fleet, the URL prefix used by fleetctl, and the redirect URL set with an identity provider.
- Default value: Empty (no prefix set)
- Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_URL_PREFIX - Config file format:
server: url_prefix: /apps/fleet
server_keepalive
Controls the server side http keep alive property.
Turning off keepalives has helped reduce outstanding TCP connections in some deployments.
- Default value: true
- Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_KEEPALIVE - Config file format:
server: keepalive: true
server_websockets_allow_unsafe_origin
Controls the servers websocket origin check. If your Fleet server is behind a reverse proxy,
the Origin header may not reflect the client's true origin. In this case, you might need to
disable the origin header (by setting this configuration to true)
check or configure your reverse proxy to forward the correct Origin header.
Setting to true will disable the origin check.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_SERVER_WEBSOCKETS_ALLOW_UNSAFE_ORIGIN - Config file format:
server: websockets_allow_unsafe_origin: true
Example YAML
server:
address: 0.0.0.0:443
password: foobar
cert: /tmp/fleet.crt
key: /tmp/fleet.key
invite_token_validity_period: 1d
Auth
auth_bcrypt_cost
The bcrypt cost to use when hashing user passwords.
- Default value:
12 - Environment variable:
FLEET_AUTH_BCRYPT_COST - Config file format:
auth: bcrypt_cost: 14
auth_salt_key_size
The key size of the salt which is generated when hashing user passwords.
- Default value:
24 - Environment variable:
FLEET_AUTH_SALT_KEY_SIZE - Config file format:
auth: salt_key_size: 36
Example YAML
auth:
bcrypt_cost: 14
salt_key_size: 36
App
app_token_key_size
Size of generated app tokens.
- Default value:
24 - Environment variable:
FLEET_APP_TOKEN_KEY_SIZE - Config file format:
app: token_key_size: 36
app_invite_token_validity_period
How long invite tokens should be valid for.
- Default value:
5 days - Environment variable:
FLEET_APP_INVITE_TOKEN_VALIDITY_PERIOD - Config file format:
app: invite_token_validity_period: 1d
app_enable_scheduled_query_stats
Determines whether Fleet gets scheduled query statistics from hosts or not.
- Default value:
true - Environment variable:
FLEET_APP_ENABLE_SCHEDULED_QUERY_STATS - Config file format:
app: enable_scheduled_query_stats: true
Example YAML
app:
token_key_size: 36
salt_key_size: 36
invite_token_validity_period: 1d
License
license_key
The license key provided to Fleet customers which provides access to Fleet Premium features.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LICENSE_KEY - Config file format:
license: key: foobar
license_enforce_host_limit
Whether Fleet should enforce the host limit of the license, if true, attempting to enroll new hosts when the limit is reached will fail.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_LICENSE_ENFORCE_HOST_LIMIT - Config file format:
license: enforce_host_limit: true
Example YAML
license:
key: foobar
enforce_host_limit: false
Session
session_key_size
The size of the session key.
- Default value:
64 - Environment variable:
FLEET_SESSION_KEY_SIZE - Config file format:
session: key_size: 48
session_duration
This is the amount of time that a session should last. Whenever a user logs in, the time is reset to the specified, or default, duration.
Valid time units are s, m, h.
- Default value:
5d(5 days) - Environment variable:
FLEET_SESSION_DURATION - Config file format:
session: duration: 4h
Example YAML
session:
duration: 4h
Osquery
osquery_node_key_size
The size of the node key which is negotiated with osqueryd clients.
- Default value:
24 - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_NODE_KEY_SIZE - Config file format:
osquery: node_key_size: 36
osquery_host_identifier
The identifier to use when determining uniqueness of hosts.
Options are provided (default), uuid, hostname, or instance.
This setting works in combination with the --host_identifier flag in osquery. In most deployments, using uuid will be the best option. The flag defaults to provided -- preserving the existing behavior of Fleet's handling of host identifiers -- using the identifier provided by osquery. instance, uuid, and hostname correspond to the same meanings as osquery's --host_identifier flag.
Users that have duplicate UUIDs in their environment can benefit from setting this flag to instance.
If you are enrolling your hosts using Fleet generated packages, it is reccommended to use
uuidas your indentifier. This prevents potential issues with duplicate host enrollments.
- Default value:
provided - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_HOST_IDENTIFIER - Config file format:
osquery: host_identifier: uuid
osquery_enroll_cooldown
The cooldown period for host enrollment. If a host (uniquely identified by the osquery_host_identifier option) tries to enroll within this duration from the last enrollment, enroll will fail.
This flag can be used to control load on the database in scenarios in which many hosts are using the same identifier. Often configuring osquery_host_identifier to instance may be a better solution.
- Default value:
0(off) - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ENROLL_COOLDOWN - Config file format:
osquery: enroll_cooldown: 1m
osquery_label_update_interval
The interval at which Fleet will ask osquery agents to update their results for label queries.
Setting this to a higher value can reduce baseline load on the Fleet server in larger deployments.
Setting this to a lower value can increase baseline load significantly and cause performance issues or even outages. Proceed with caution.
Valid time units are s, m, h.
- Default value:
1h - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_LABEL_UPDATE_INTERVAL - Config file format:
osquery: label_update_interval: 90m
osquery_policy_update_interval
The interval at which Fleet will ask osquery agents to update their results for policy queries.
Setting this to a higher value can reduce baseline load on the Fleet server in larger deployments.
Setting this to a lower value can increase baseline load significantly and cause performance issues or even outages. Proceed with caution.
Valid time units are s, m, h.
- Default value:
1h - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_POLICY_UPDATE_INTERVAL - Config file format:
osquery: policy_update_interval: 90m
osquery_detail_update_interval
The interval at which Fleet will ask osquery agents to update host details (such as uptime, hostname, network interfaces, etc.)
Setting this to a higher value can reduce baseline load on the Fleet server in larger deployments.
Setting this to a lower value can increase baseline load significantly and cause performance issues or even outages. Proceed with caution.
Valid time units are s, m, h.
- Default value:
1h - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_DETAIL_UPDATE_INTERVAL - Config file format:
osquery: detail_update_interval: 90m
osquery_status_log_plugin
This is the log output plugin that should be used for osquery status logs received from clients. Check out the reference documentation for log destinations.
Options are filesystem, firehose, kinesis, lambda, pubsub, kafkarest, and stdout.
- Default value:
filesystem - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_STATUS_LOG_PLUGIN - Config file format:
osquery: status_log_plugin: firehose
osquery_result_log_plugin
This is the log output plugin that should be used for osquery result logs received from clients. Check out the reference documentation for log destinations.
Options are filesystem, firehose, kinesis, lambda, pubsub, kafkarest, and stdout.
- Default value:
filesystem - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_RESULT_LOG_PLUGIN - Config file format:
osquery: result_log_plugin: firehose
osquery_max_jitter_percent
Given an update interval (label, or details), this will add up to the defined percentage in randomness to the interval.
The goal of this is to prevent all hosts from checking in with data at the same time.
So for example, if the label_update_interval is 1h, and this is set to 10. It'll add up a random number between 0 and 6 minutes to the amount of time it takes for Fleet to give the host the label queries.
- Default value:
10 - Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_MAX_JITTER_PERCENT - Config file format:
osquery: max_jitter_percent: 10
osquery_enable_async_host_processing
Experimental feature. Enable asynchronous processing of hosts' query results. Currently, asyncronous processing is only supported for label query execution, policy membership results, hosts' last seen timestamp, and hosts' scheduled query statistics. This may improve the performance and CPU usage of the Fleet instances and MySQL database servers for setups with a large number of hosts while requiring more resources from Redis server(s).
Note that currently, if both the failing policies webhook and this osquery.enable_async_host_processing option are set, some failing policies webhooks could be missing (some transitions from succeeding to failing or vice-versa could happen without triggering a webhook request).
It can be set to a single boolean value ("true" or "false"), which controls all async host processing tasks, or it can be set for specific async tasks using a syntax similar to an URL query string or parameters in a Data Source Name (DSN) string, e.g., "label_membership=true&policy_membership=true". When using the per-task syntax, omitted tasks get the default value. The supported async task names are:
label_membershipfor updating the hosts' label query execution;policy_membershipfor updating the hosts' policy membership results;host_last_seenfor updating the hosts' last seen timestamp.scheduled_query_statsfor saving the hosts' scheduled query statistics.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ENABLE_ASYNC_HOST_PROCESSING - Config file format:
osquery: enable_async_host_processing: true
osquery_async_host_collect_interval
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Sets the interval at which the host data will be collected into the database. Each Fleet instance will attempt to do the collection at this interval (with some optional jitter added, see osquery_async_host_collect_max_jitter_percent), with only one succeeding to get the exclusive lock.
It can be set to a single duration value (e.g., "30s"), which defines the interval for all async host processing tasks, or it can be set for specific async tasks using a syntax similar to an URL query string or parameters in a Data Source Name (DSN) string, e.g., "label_membership=10s&policy_membership=1m". When using the per-task syntax, omitted tasks get the default value. See osquery_enable_async_host_processing for the supported async task names.
- Default value: 30s
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_COLLECT_INTERVAL - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_collect_interval: 1m
osquery_async_host_collect_max_jitter_percent
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. A number interpreted as a percentage of osquery_async_host_collect_interval to add to (or remove from) the interval so that not all hosts try to do the collection at the same time.
- Default value: 10
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_COLLECT_MAX_JITTER_PERCENT - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_collect_max_jitter_percent: 5
osquery_async_host_collect_lock_timeout
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Timeout of the lock acquired by a Fleet instance to collect host data into the database. If the collection runs for too long or the instance crashes unexpectedly, the lock will be automatically released after this duration and another Fleet instance can proceed with the next collection.
It can be set to a single duration value (e.g., "1m"), which defines the lock timeout for all async host processing tasks, or it can be set for specific async tasks using a syntax similar to an URL query string or parameters in a Data Source Name (DSN) string, e.g., "label_membership=2m&policy_membership=5m". When using the per-task syntax, omitted tasks get the default value. See osquery_enable_async_host_processing for the supported async task names.
- Default value: 1m
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_COLLECT_LOCK_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_collect_lock_timeout: 5m
osquery_async_host_collect_log_stats_interval
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Interval at which the host collection statistics are logged, 0 to disable logging of statistics. Note that logging is done at the "debug" level.
- Default value: 1m
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_COLLECT_LOG_STATS_INTERVAL - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_collect_log_stats_interval: 5m
osquery_async_host_insert_batch
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Size of the INSERT batch when collecting host data into the database.
- Default value: 2000
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_INSERT_BATCH - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_insert_batch: 1000
osquery_async_host_delete_batch
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Size of the DELETE batch when collecting host data into the database.
- Default value: 2000
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_DELETE_BATCH - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_delete_batch: 1000
osquery_async_host_update_batch
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Size of the UPDATE batch when collecting host data into the database.
- Default value: 1000
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_UPDATE_BATCH - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_update_batch: 500
osquery_async_host_redis_pop_count
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Maximum number of items to pop from a redis key at a time when collecting host data into the database.
- Default value: 1000
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_REDIS_POP_COUNT - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_redis_pop_count: 500
osquery_async_host_redis_scan_keys_count
Applies only when osquery_enable_async_host_processing is enabled. Order of magnitude (e.g., 10, 100, 1000, etc.) of set members to scan in a single ZSCAN/SSCAN request for items to process when collecting host data into the database.
- Default value: 1000
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_ASYNC_HOST_REDIS_SCAN_KEYS_COUNT - Config file format:
osquery: async_host_redis_scan_keys_count: 100
osquery_min_software_last_opened_at_diff
The minimum time difference between the software's "last opened at" timestamp reported by osquery and the last timestamp saved for that software on that host helps minimize the number of updates required when a host reports its installed software information, resulting in less load on the database. If there is no existing timestamp for the software on that host (or if the software was not installed on that host previously), the new timestamp is automatically saved.
- Default value: 1h
- Environment variable:
FLEET_OSQUERY_MIN_SOFTWARE_LAST_OPENED_AT_DIFF - Config file format:
osquery: min_software_last_opened_at_diff: 4h
Example YAML
osquery:
host_identifier: uuid
policy_update_interval: 30m
duration: 4h
status_log_plugin: firehose
result_log_plugin: firehose
External Activity Audit Logging
Applies only to Fleet Premium. Acitivity information is available for all Fleet instances using the Activities API.
Stream Fleet user activities to logs using Fleet's logging plugins. The audit events are logged in an asynchronous fashion. It can take up to 5 minutes for an event to be logged.
activity_enable_audit_log
This enables/disables the log output for audit events.
See the activity_audit_log_plugin option below that specifies the logging destination.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_ACTIVITY_ENABLE_AUDIT_LOG - Config file format:
activity: enable_audit_log: true
activity_audit_log_plugin
This is the log output plugin that should be used for audit logs.
This flag only has effect if activity_enable_audit_log is set to true.
Each plugin has additional configuration options. Please see the configuration section linked below for your logging plugin.
Options are filesystem, firehose, kinesis, lambda, pubsub, kafkarest, and stdout (no additional configuration needed).
- Default value:
filesystem - Environment variable:
FLEET_ACTIVITY_AUDIT_LOG_PLUGIN - Config file format:
activity: audit_log_plugin: firehose
Logging (Fleet server logging)
logging_debug
Whether or not to enable debug logging.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_LOGGING_DEBUG - Config file format:
logging: debug: true
logging_json
Whether or not to log in JSON.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_LOGGING_JSON - Config file format:
logging: json: true
logging_disable_banner
Whether or not to log the welcome banner.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_LOGGING_DISABLE_BANNER - Config file format:
logging: disable_banner: true
logging_error_retention_period
The amount of time to keep an error. Unique instances of errors are stored temporarily to help with troubleshooting, this setting controls that duration. Set to 0 to keep them without expiration, and a negative value to disable storage of errors in Redis.
- Default value: 24h
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LOGGING_ERROR_RETENTION_PERIOD - Config file format:
logging: error_retention_period: 1h
Example YAML
logging:
disable_banner: true
policy_update_interval: 30m
error_retention_period: 1h
Filesystem
filesystem_status_log_file
This flag only has effect if osquery_status_log_plugin is set to filesystem (the default value).
The path which osquery status logs will be logged to.
- Default value:
/tmp/osquery_status - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_STATUS_LOG_FILE - Config file format:
filesystem: status_log_file: /var/log/osquery/status.log
filesystem_result_log_file
This flag only has effect if osquery_result_log_plugin is set to filesystem (the default value).
The path which osquery result logs will be logged to.
- Default value:
/tmp/osquery_result - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_RESULT_LOG_FILE - Config file format:
filesystem: result_log_file: /var/log/osquery/result.log
filesystem_audit_log_file
This flag only has effect if activity_audit_log_plugin is set to filesystem (the default value) and if activity_enable_audit_log is set to true.
The path which audit logs will be logged to.
- Default value:
/tmp/audit - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_AUDIT_LOG_FILE - Config file format:
filesystem: audit_log_file: /var/log/fleet/audit.log
filesystem_enable_log_rotation
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tofilesystem(the default value).activity_audit_log_pluginis set tofilesystemandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
This flag will cause the osquery result and status log files to be automatically rotated when files reach a size of 500 Mb or an age of 28 days.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_ENABLE_LOG_ROTATION - Config file format:
filesystem: enable_log_rotation: true
filesystem_enable_log_compression
This flag only has effect if filesystem_enable_log_rotation is set to true.
This flag will cause the rotated logs to be compressed with gzip.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_ENABLE_LOG_COMPRESSION - Config file format:
filesystem: enable_log_compression: true
filesystem_max_size
This flag only has effect if filesystem_enable_log_rotation is set to true.
Sets the maximum size in megabytes of log files before it gets rotated.
- Default value:
500 - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_MAX_SIZE - Config file format:
filesystem: max_size: 100
filesystem_max_age
This flag only has effect if filesystem_enable_log_rotation is set to true.
Sets the maximum age in days to retain old log files before deletion. Setting this to zero will retain all logs.
- Default value:
28 - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_MAX_AGE - Config file format:
filesystem: max_age: 0
filesystem_max_backups
This flag only has effect if filesystem_enable_log_rotation is set to true.
Sets the maximum number of old files to retain before deletion. Setting this to zero will retain all logs. Note max_age may still cause them to be deleted.
- Default value:
3 - Environment variable:
FLEET_FILESYSTEM_MAX_BACKUPS - Config file format:
filesystem: max_backups: 0
Example YAML
osquery:
osquery_status_log_plugin: filesystem
osquery_result_log_plugin: filesystem
filesystem:
status_log_file: /var/log/osquery/status.log
result_log_file: /var/log/osquery/result.log
enable_log_rotation: true
Firehose
firehose_region
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tofirehose.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tofirehoseandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS region to use for Firehose connection.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_FIREHOSE_REGION - Config file format:
firehose: region: ca-central-1
firehose_access_key_id
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tofirehose.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tofirehoseandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
If firehose_access_key_id and firehose_secret_access_key are omitted, Fleet will try to use AWS STS credentials.
AWS access key ID to use for Firehose authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_FIREHOSE_ACCESS_KEY_ID - Config file format:
firehose: access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
firehose_secret_access_key
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tofirehose.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tofirehoseandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS secret access key to use for Firehose authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_FIREHOSE_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY - Config file format:
firehose: secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
firehose_sts_assume_role_arn
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tofirehose.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tofirehoseandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS STS role ARN to use for Firehose authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_FIREHOSE_STS_ASSUME_ROLE_ARN - Config file format:
firehose: sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/firehose-role
firehose_status_stream
This flag only has effect if osquery_status_log_plugin is set to firehose.
Name of the Firehose stream to write osquery status logs received from clients.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_FIREHOSE_STATUS_STREAM - Config file format:
firehose: status_stream: osquery_status
The IAM role used to send to Firehose must allow the following permissions on the stream listed:
firehose:DescribeDeliveryStreamfirehose:PutRecordBatch
firehose_result_stream
This flag only has effect if osquery_result_log_plugin is set to firehose.
Name of the Firehose stream to write osquery result logs received from clients.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_FIREHOSE_RESULT_STREAM - Config file format:
firehose: result_stream: osquery_result
The IAM role used to send to Firehose must allow the following permissions on the stream listed:
firehose:DescribeDeliveryStreamfirehose:PutRecordBatch
firehose_audit_stream
This flag only has effect if activity_audit_log_plugin is set to firehose.
Name of the Firehose stream to audit logs.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_FIREHOSE_AUDIT_STREAM - Config file format:
firehose: audit_stream: fleet_audit
The IAM role used to send to Firehose must allow the following permissions on the stream listed:
firehose:DescribeDeliveryStreamfirehose:PutRecordBatch
Example YAML
osquery:
osquery_status_log_plugin: firehose
osquery_result_log_plugin: firehose
firehose:
region: ca-central-1
access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/firehose-role
status_stream: osquery_status
result_stream: osquery_result
Kinesis
kinesis_region
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tokinesis.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tokinesisandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS region to use for Kinesis connection
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KINESIS_REGION - Config file format:
kinesis: region: ca-central-1
kinesis_access_key_id
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tokinesis.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tokinesisandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
If kinesis_access_key_id and kinesis_secret_access_key are omitted, Fleet
will try to use
AWS STS
credentials.
AWS access key ID to use for Kinesis authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KINESIS_ACCESS_KEY_ID - Config file format:
kinesis: access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
kinesis_secret_access_key
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tokinesis.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tokinesisandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS secret access key to use for Kinesis authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KINESIS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY - Config file format:
kinesis: secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
kinesis_sts_assume_role_arn
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tokinesis.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tokinesisandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS STS role ARN to use for Kinesis authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KINESIS_STS_ASSUME_ROLE_ARN - Config file format:
kinesis: sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/kinesis-role
kinesis_status_stream
This flag only has effect if osquery_status_log_plugin is set to kinesis.
Name of the Kinesis stream to write osquery status logs received from clients.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KINESIS_STATUS_STREAM - Config file format:
kinesis: status_stream: osquery_status
The IAM role used to send to Kinesis must allow the following permissions on the stream listed:
kinesis:DescribeStreamkinesis:PutRecords
kinesis_result_stream
This flag only has effect if osquery_result_log_plugin is set to kinesis.
Name of the Kinesis stream to write osquery result logs received from clients.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KINESIS_RESULT_STREAM - Config file format:
kinesis: result_stream: osquery_result
The IAM role used to send to Kinesis must allow the following permissions on the stream listed:
kinesis:DescribeStreamkinesis:PutRecords
kinesis_audit_stream
This flag only has effect if activity_audit_log_plugin is set to kinesis.
Name of the Kinesis stream to write audit logs.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KINESIS_AUDIT_STREAM - Config file format:
kinesis: audit_stream: fleet_audit
The IAM role used to send to Kinesis must allow the following permissions on the stream listed:
kinesis:DescribeStreamkinesis:PutRecords
Example YAML
osquery:
osquery_status_log_plugin: kinesis
osquery_result_log_plugin: kinesis
kinesis:
region: ca-central-1
access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/firehose-role
status_stream: osquery_status
result_stream: osquery_result
Lambda
lambda_region
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tolambda.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tolambdaandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS region to use for Lambda connection.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LAMBDA_REGION - Config file format:
lambda: region: ca-central-1
lambda_access_key_id
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tolambda.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tolambdaandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
If lambda_access_key_id and lambda_secret_access_key are omitted, Fleet
will try to use
AWS STS
credentials.
AWS access key ID to use for Lambda authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LAMBDA_ACCESS_KEY_ID - Config file format:
lambda: access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
lambda_secret_access_key
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tolambda.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tolambdaandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS secret access key to use for Lambda authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LAMBDA_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY - Config file format:
lambda: secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
lambda_sts_assume_role_arn
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tolambda.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tolambdaandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
AWS STS role ARN to use for Lambda authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LAMBDA_STS_ASSUME_ROLE_ARN - Config file format:
lambda: sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/lambda-role
lambda_status_function
This flag only has effect if osquery_status_log_plugin is set to lambda.
Name of the Lambda function to write osquery status logs received from clients.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LAMBDA_STATUS_FUNCTION - Config file format:
lambda: status_function: statusFunction
The IAM role used to send to Lambda must allow the following permissions on the function listed:
lambda:InvokeFunction
lambda_result_function
This flag only has effect if osquery_result_log_plugin is set to lambda.
Name of the Lambda function to write osquery result logs received from clients.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LAMBDA_RESULT_FUNCTION - Config file format:
lambda: result_function: resultFunction
The IAM role used to send to Lambda must allow the following permissions on the function listed:
lambda:InvokeFunction
lambda_audit_function
This flag only has effect if activity_audit_log_plugin is set to lambda.
Name of the Lambda function to write audit logs.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_LAMBDA_AUDIT_FUNCTION - Config file format:
lambda: audit_function: auditFunction
The IAM role used to send to Lambda must allow the following permissions on the function listed:
lambda:InvokeFunction
Example YAML
osquery:
osquery_status_log_plugin: lambda
osquery_result_log_plugin: lambda
lambda:
region: ca-central-1
access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/firehose-role
status_function: statusFunction
result_function: resultFunction
PubSub
pubsub_project
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set topubsub.activity_audit_log_pluginis set topubsubandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
The identifier of the Google Cloud project containing the pubsub topics to publish logs to.
Note that the pubsub plugin uses Application Default Credentials (ADCs) for authentication with the service.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PUBSUB_PROJECT - Config file format:
pubsub: project: my-gcp-project
pubsub_result_topic
This flag only has effect if osquery_result_log_plugin is set to pubsub.
The identifier of the pubsub topic that client results will be published to.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PUBSUB_RESULT_TOPIC - Config file format:
pubsub: result_topic: osquery_result
pubsub_status_topic
This flag only has effect if osquery_status_log_plugin is set to pubsub.
The identifier of the pubsub topic that osquery status logs will be published to.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PUBSUB_STATUS_TOPIC - Config file format:
pubsub: status_topic: osquery_status
pubsub_audit_topic
This flag only has effect if osquery_audit_log_plugin is set to pubsub.
The identifier of the pubsub topic that client results will be published to.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PUBSUB_AUDIT_TOPIC - Config file format:
pubsub: audit_topic: fleet_audit
pubsub_add_attributes
This flag only has effect if osquery_status_log_plugin is set to pubsub.
Add Pub/Sub attributes to messages. When enabled, the plugin parses the osquery result messages, and adds the following Pub/Sub message attributes:
name- thenameattribute from the message bodytimestamp- theunixTimeattribute from the message body, converted to rfc3339 format- Each decoration from the message
This feature is useful when combined with subscription filters.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PUBSUB_ADD_ATTRIBUTES - Config file format:
pubsub: add_attributes: true
Example YAML
osquery:
osquery_status_log_plugin: pubsub
osquery_result_log_plugin: pubsub
pubsub:
project: my-gcp-project
result_topic: osquery_result
status_topic: osquery_status
sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/firehose-role
status_function: statusFunction
result_function: resultFunction
Kafka REST Proxy logging
kafkarest_proxyhost
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tokafkarest.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tokafkarestandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
The URL of the host which to check for the topic existence and post messages to the specified topic.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KAFKAREST_PROXYHOST - Config file format:
kafkarest: proxyhost: "https://localhost:8443"
kafkarest_status_topic
This flag only has effect if osquery_status_log_plugin is set to kafkarest.
The identifier of the kafka topic that osquery status logs will be published to.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KAFKAREST_STATUS_TOPIC - Config file format:
kafkarest: status_topic: osquery_status
kafkarest_result_topic
This flag only has effect if osquery_result_log_plugin is set to kafkarest.
The identifier of the kafka topic that osquery result logs will be published to.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KAFKAREST_RESULT_TOPIC - Config file format:
kafkarest: result_topic: osquery_result
kafkarest_audit_topic
This flag only has effect if osquery_audit_log_plugin is set to kafkarest.
The identifier of the kafka topic that audit logs will be published to.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KAFKAREST_AUDIT_TOPIC - Config file format:
kafkarest: audit_topic: fleet_audit
kafkarest_timeout
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tokafkarest.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tokafkarestandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
The timeout value for the http post attempt. Value is in units of seconds.
- Default value: 5
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KAFKAREST_TIMEOUT - Config file format:
kafkarest: timeout: 5
kafkarest_content_type_value
This flag only has effect if one of the following is true:
osquery_result_log_pluginorosquery_status_log_pluginare set tokafkarest.activity_audit_log_pluginis set tokafkarestandactivity_enable_audit_logis set totrue.
The value of the Content-Type header to use in Kafka REST Proxy API calls. More information about available versions can be found here. Note: only JSON format is supported
- Default value: application/vnd.kafka.json.v1+json
- Environment variable:
FLEET_KAFKAREST_CONTENT_TYPE_VALUE - Config file format:
kafkarest: content_type_value: application/vnd.kafka.json.v2+json
Example YAML
osquery:
osquery_status_log_plugin: kafkarest
osquery_result_log_plugin: kafkarest
kafkarest:
proxyhost: "https://localhost:8443"
result_topic: osquery_result
status_topic: osquery_status
S3 file carving backend
s3_bucket
Name of the S3 bucket to use to store file carves.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_BUCKET - Config file format:
s3: bucket: some-carve-bucket
s3_prefix
Prefix to prepend to carve objects.
All carve objects will also be prefixed by date and hour (UTC), making the resulting keys look like: <prefix><year>/<month>/<day>/<hour>/<carve-name>.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_PREFIX - Config file format:
s3: prefix: carves-go-here/
s3_access_key_id
AWS access key ID to use for S3 authentication.
If s3_access_key_id and s3_secret_access_key are omitted, Fleet will try to use
the default credential provider chain.
The IAM identity used in this context must be allowed to perform the following actions on the bucket: s3:PutObject, s3:GetObject, s3:ListMultipartUploadParts, s3:ListBucket, s3:GetBucketLocation.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_ACCESS_KEY_ID - Config file format:
s3: access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
s3_secret_access_key
AWS secret access key to use for S3 authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY - Config file format:
s3: secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
s3_sts_assume_role_arn
AWS STS role ARN to use for S3 authentication.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_STS_ASSUME_ROLE_ARN - Config file format:
s3: sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/some-s3-role
s3_endpoint_url
AWS S3 Endpoint URL. Override when using a different S3 compatible object storage backend (such as Minio), or running s3 locally with localstack. Leave this blank to use the default S3 service endpoint.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_ENDPOINT_URL - Config file format:
s3: endpoint_url: http://localhost:9000
s3_disable_ssl
AWS S3 Disable SSL. Useful for local testing.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_DISABLE_SSL - Config file format:
s3: disable_ssl: false
s3_force_s3_path_style
AWS S3 Force S3 Path Style. Set this to true to force the request to use path-style addressing,
i.e., http://s3.amazonaws.com/BUCKET/KEY. By default, the S3 client
will use virtual hosted bucket addressing when possible
(http://BUCKET.s3.amazonaws.com/KEY).
See here for details.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_FORCE_S3_PATH_STYLE - Config file format:
s3: force_s3_path_style: false
s3_region
AWS S3 Region. Leave blank to enable region discovery.
Minio users must set this to any nonempty value (eg. minio), as Minio does not support region discovery.
- Default value:
- Environment variable:
FLEET_S3_REGION - Config file format:
s3: region: us-east-1
Example YAML
s3:
bucket: some-carve-bucket
prefix: carves-go-here/
access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/some-s3-role
region: us-east-1
Upgrades
allow_missing_migrations
If set then fleet serve will run even if there are database migrations missing.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_UPGRADES_ALLOW_MISSING_MIGRATIONS - Config file format:
upgrades: allow_missing_migrations: true
Vulnerabilities
databases_path
The path specified needs to exist and Fleet needs to be able to read and write to and from it. This is the only mandatory configuration needed for vulnerability processing to work.
When current_instance_checks is set to auto (the default), Fleet instances will try to create the databases_path if it doesn't exist.
- Default value:
/tmp/vulndbs - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_DATABASES_PATH - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: databases_path: /some/path
periodicity
How often vulnerabilities are checked. This is also the interval at which the counts of hosts per software is calculated.
- Default value:
1h - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_PERIODICITY - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: periodicity: 1h
cpe_database_url
You can fetch the CPE dictionary database from this URL. Some users want to control where Fleet gets its database. When Fleet sees this value defined, it downloads the file directly. It expects a file in the same format that can be found in https://github.com/fleetdm/nvd/releases. If this value is not defined, Fleet checks for the latest release in Github and only downloads it if needed.
- Default value:
"" - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_CPE_DATABASE_URL - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: cpe_database_url: ""
cpe_translations_url
You can fetch the CPE translations from this URL. Translations are used when matching software to CPE entries in the CPE database that would otherwise be missed for various reasons. When Fleet sees this value defined, it downloads the file directly. It expects a file in the same format that can be found in https://github.com/fleetdm/nvd/releases. If this value is not defined, Fleet checks for the latest release in Github and only downloads it if needed.
- Default value:
"" - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_CPE_TRANSLATIONS_URL - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: cpe_translations_url: ""
cve_feed_prefix_url
Like the CPE dictionary, we allow users to define where to get the CVE feeds. In this case, the URL should be a host that serves the files in the path /feeds/json/cve/1.1/. Fleet expects to find all the JSON Feeds that can be found in https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/data-feeds. When not defined, Fleet downloads from the nvd.nist.gov host.
- Default value:
"" - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_CVE_FEED_PREFIX_URL - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: cve_feed_prefix_url: ""
current_instance_checks
When running multiple instances of the Fleet server, by default, one of them dynamically takes the lead in vulnerability processing. This lead can change over time. Some Fleet users want to be able to define which deployment is doing this checking. If you wish to do this, you'll need to deploy your Fleet instances with this set explicitly to no and one of them set to yes.
- Default value:
auto - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_CURRENT_INSTANCE_CHECKS - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: current_instance_checks: yes
disable_schedule
To externally manage running vulnerability processing set the value to true and then run fleet vuln_processing using external
tools like crontab.
- Default value:
false - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_DISABLE_SCHEDULE - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: disable_schedule: false
disable_data_sync
Fleet by default automatically downloads and keeps the different data streams needed to properly do vulnerability processing. In some setups, this behavior is not wanted, as access to outside resources might be blocked, or the data stream files might need review/audit before use.
In order to support vulnerability processing in such environments, we allow users to disable automatic sync of data streams with this configuration value.
To download the data streams, you can use fleetctl vulnerability-data-stream --dir ./somedir. The contents downloaded can then be reviewed, and finally uploaded to the defined databases_path in the fleet instance(s) doing the vulnerability processing.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_DISABLE_DATA_SYNC - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: disable_data_sync: true
recent_vulnerability_max_age
Maximum age of a vulnerability (a CVE) to be considered "recent". The age is calculated based on the published date of the CVE in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD). Recent vulnerabilities play a special role in Fleet's automations, as they are reported when discovered on a host if the vulnerabilities webhook or a vulnerability integration is enabled.
- Default value:
720h(30 days) - Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_RECENT_VULNERABILITY_MAX_AGE - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: recent_vulnerability_max_age: 48h
disable_win_os_vulnerabilities
If using osquery 5.4 or later, Fleet by default will fetch and store all applied Windows updates and use that for detecting Windows vulnerabilities — which might be a writing-intensive process (depending on the number of Windows hosts in your Fleet). Setting this to true will cause Fleet to skip both processes.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_VULNERABILITIES_DISABLE_WIN_OS_VULNERABILITIES - Config file format:
vulnerabilities: disable_win_os_vulnerabilities: true
Example YAML
vulnerabilities:
databases_path: /some/path
current_instance_checks: yes
disable_data_sync: true
GeoIP
database_path
The path to a valid Maxmind GeoIP database(mmdb). Support exists for the country & city versions of the database. If city database is supplied
then Fleet will attempt to resolve the location via the city lookup, otherwise it defaults to the country lookup. The IP address used
to determine location is extracted via HTTP headers in the following order: True-Client-IP, X-Real-IP, and finally X-FORWARDED-FOR headers
on the Fleet web server.
- Default value: none
- Environment variable:
FLEET_GEOIP_DATABASE_PATH - Config file format:
geoip: database_path: /some/path
Sentry
DSN
If set, then Fleet serve will capture errors and panics and push them to Sentry.
- Default value:
"" - Environment variable:
FLEET_SENTRY_DSN - Config file format:
sentry: dsn: "https://somedsnprovidedby.sentry.com/"
Prometheus
basic_auth.username
This is the username to use for HTTP Basic Auth on the /metrics endpoint.
If basic_auth.username is not set, then:
-
If
basic_auth.disableis not set then the Prometheus/metricsendpoint is disabled. -
If
basic_auth.disableis set then the Prometheus/metricsendpoint is enabled but without HTTP Basic Auth. -
Default value:
"" -
Environment variable:
FLEET_PROMETHEUS_BASIC_AUTH_USERNAME -
Config file format:
prometheus: basic_auth: username: "foo"
basic_auth.password
This is the password to use for HTTP Basic Auth on the /metrics endpoint.
If basic_auth.password is not set, then:
-
If
basic_auth.disableis not set then the Prometheus/metricsendpoint is disabled. -
If
basic_auth.disableis set then the Prometheus/metricsendpoint is enabled but without HTTP Basic Auth. -
Default value:
"" -
Environment variable:
FLEET_PROMETHEUS_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD -
Config file format:
prometheus: basic_auth: password: "bar"
basic_auth.disable
This allows running the Prometheus endpoint /metrics without HTTP Basic Auth.
If both basic_auth.username and basic_auth.password are set, then this setting is ignored.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PROMETHEUS_BASIC_AUTH_DISABLE - Config file format:
prometheus: basic_auth: disable: true
Packaging
These configurations control how Fleet interacts with the packaging server (coming soon). These features are currently only intended to be used within Fleet sandbox, but this is subject to change.
packaging_global_enroll_secret
This is the enroll secret for adding hosts to the global scope. If this value is set, the server won't allow changes to the enroll secret via the config endpoints.
This value should be treated as a secret. We recommend using a
cryptographically secure pseudo random string. For example, using openssl:
openssl rand -base64 24
This config only takes effect if you don't have a global enroll secret already stored in your database.
- Default value:
"" - Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_GLOBAL_ENROLL_SECRET - Config file format:
packaging: global_enroll_secret: "xyz"
packaging_s3_bucket
This is the name of the S3 bucket to store pre-built Orbit installers.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_BUCKET - Config file format:
packaging: s3: bucket: some-bucket
packaging_s3_prefix
This is the prefix to prepend when searching for installers.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_PREFIX - Config file format:
packaging: s3: prefix: installers-go-here/
packaging_s3_access_key_id
This is the AWS access key ID for S3 authentication.
If s3_access_key_id and s3_secret_access_key are omitted, Fleet will try to use
the default credential provider chain.
The IAM identity used in this context must be allowed to perform the following actions on the bucket: s3:GetObject, s3:ListBucket.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_ACCESS_KEY_ID - Config file format:
packaging: s3: access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
packaging_s3_secret_access_key
This is the AWS secret access key for S3 authentication.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY - Config file format:
packaging: s3: secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
packaging_s3_sts_assume_role_arn
This is the AWS STS role ARN for S3 authentication.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_STS_ASSUME_ROLE_ARN - Config file format:
packaging: s3: sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/some-s3-role
packaging_s3_endpoint_url
This is the AWS S3 Endpoint URL. Override when using a different S3 compatible object storage backend (such as Minio) or running S3 locally with LocalStack. Leave this blank to use the default AWS S3 service endpoint.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_ENDPOINT_URL - Config file format:
packaging: s3: endpoint_url: http://localhost:9000
packaging_s3_disable_ssl
This is the AWS S3 Disable SSL. It's useful for local testing.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_DISABLE_SSL - Config file format:
packaging: s3: disable_ssl: false
packaging_s3_force_s3_path_style
This is the AWS S3 Force S3 Path Style. Set this to true to force the request to use path-style addressing
(e.g., http://s3.amazonaws.com/BUCKET/KEY). By default, the S3 client
will use virtual hosted bucket addressing when possible
(http://BUCKET.s3.amazonaws.com/KEY).
See the Virtual hosting of buckets doc for details.
- Default value: false
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_FORCE_S3_PATH_STYLE - Config file format:
packaging: s3: force_s3_path_style: false
packaging_s3_region
This is the AWS S3 Region. Leave it blank to enable region discovery.
Minio users must set this to any non-empty value (e.g., minio), as Minio does not support region discovery.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_PACKAGING_S3_REGION - Config file format:
packaging: s3: region: us-east-1
Example YAML
packaging:
s3:
bucket: some-bucket
prefix: installers-go-here/
access_key_id: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
secret_access_key: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
sts_assume_role_arn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/some-s3-role
region: us-east-1
Mobile device management (MDM)
MDM features are not ready for production and are currently in beta. These features are disabled by default. To enable these features set
FLEET_DEV_MDM_ENABLED=1as an environment variable.
MDM features require some endpoints to be publicly accessible outside your VPN or intranet, for more details see What API endpoints should I expose to the public internet?
This section is a reference for the configuration required to turn on MDM features in production.
If you're a Fleet contributor and you'd like to turn on MDM features in a local environment, see the guided instructions here.
mdm.apple_enable
This is the second feature flag required to turn on MDM features. This environment variable flag must be set to 1 (or true in the yaml) at the same time as when you set the certificate and keys for Apple Push Certificate server (APNs) and Apple Business Manager (ABM). Otherwise, the Fleet server won't start.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_ENABLE - Config file format:
mdm: apple_enable: true
mdm.apple_apns_cert_bytes
The content of the Apple Push Notification service (APNs) certificate. An X.509 certificate, PEM-encoded. Typically generated via fleetctl generate mdm-apple.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_APNS_CERT_BYTES - Config file format:
mdm: apple_apns_cert_bytes: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... PEM-encoded content ... -----END CERTIFICATE-----
mdm.apple_apns_key_bytes
The content of the PEM-encoded private key for the Apple Push Notification service (APNs). Typically generated via fleetctl generate mdm-apple.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_APNS_KEY_BYTES - Config file format:
mdm: apple_apns_key_bytes: | -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- ... PEM-encoded content ... -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
mdm.apple_scep_cert_bytes
The content of the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) certificate. An X.509 certificate, PEM-encoded. Typically generated via fleetctl generate mdm-apple.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_SCEP_CERT_BYTES - Config file format:
mdm: apple_scep_cert_bytes: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... PEM-encoded content ... -----END CERTIFICATE-----
mdm.apple_scep_key_bytes
The content of the PEM-encoded private key for the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP). Typically generated via fleetctl generate mdm-apple.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_SCEP_KEY_BYTES - Config file format:
mdm: apple_scep_key_bytes: | -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- ... PEM-encoded content ... -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
mdm.apple_scep_challenge
An alphanumeric secret for the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP). Should be 32 characters in length and only include alphanumeric characters.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_SCEP_CHALLENGE - Config file format:
mdm: apple_scep_challenge: scepchallenge
mdm.apple_scep_signer_validity_days
The number of days the signed SCEP client certificates will be valid.
- Default value: 365
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_SCEP_SIGNER_VALIDITY_DAYS - Config file format:
mdm: apple_scep_signer_validity_days: 100
mdm.apple_scep_signer_allow_renewal_days
The number of days allowed to renew SCEP certificates.
- Default value: 14
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_SCEP_SIGNER_ALLOW_RENEWAL_DAYS - Config file format:
mdm: apple_scep_signer_allow_renewal_days: 30
mdm.apple_bm_server_token_bytes
This is the content of the Apple Business Manager encrypted server token downloaded from Apple Business Manager.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_BM_SERVER_TOKEN_BYTES - Config file format:
mdm: apple_bm_server_token_bytes: | Content-Type: application/pkcs7-mime; name="smime.p7m"; smime-type=enveloped-data Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64 ... rest of content ...
mdm.apple_bm_cert_bytes
This is the content of the Apple Business Manager certificate. The certificate is a PEM-encoded X.509 certificate that's typically generated via fleetctl generate mdm-apple-bm.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_BM_CERT_BYTES - Config file format:
mdm: apple_bm_cert_bytes: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... PEM-encoded content ... -----END CERTIFICATE-----
mdm.apple_bm_key_bytes
This is the content of the PEM-encoded private key for the Apple Business Manager. It's typically generated via fleetctl generate mdm-apple-bm.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_APPLE_BM_KEY_BYTES - Config file format:
mdm: apple_bm_key_bytes: | -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- ... PEM-encoded content ... -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
mdm.okta_server_url
This is the URL of your Okta authorization server
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable:
FLEET_MDM_OKTA_SERVER_URL - Config file format:
mdm: okta_server_url: https://example.okta.com
##### mdm.okta_client_id
This is the client ID of the Okta application that will be used to authenticate users. This value can be found in the Okta admin page under "Applications > Client Credentials."
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable: `FLEET_MDM_OKTA_CLIENT_ID`
- Config file format:
mdm: okta_client_id: 9oa4eoxample2rpdi1087
##### mdm.okta_client_secret
This is the client secret of the Okta application that will be used to authenticate users. This value can be found in the Okta admin page under "Applications > Client Credentials."
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable: `FLEET_MDM_OKTA_CLIENT_SECRET`
- Config file format:
mdm: okta_client_secret: COp8o5zskEQ0OylgjqTrd0xu7rQLx-VteaQW4YGf
##### mdm.eula_url
An URL containing a PDF file that will be used as an EULA during DEP onboarding.
- Default value: ""
- Environment variable: `FLEET_MDM_OKTA_EULA_URL`
- Config file format:
mdm: eula_url: https://example.com/eula.pdf
##### mdm.apple_dep_sync_periodicity
The duration between DEP device syncing (fetching and setting of DEP profiles). Only relevant if Apple Business Manager (ABM) is configured.
- Default value: 1m
- Environment variable: `FLEET_MDM_APPLE_DEP_SYNC_PERIODICITY`
- Config file format:
mdm: apple_dep_sync_periodicity: 10m
##### Example YAML
```yaml
mdm:
apple_enable: true
apple_apns_cert: /path/to/apns_cert
apple_apns_key: /path/to/apns_key
apple_scep_cert: /path/to/scep_cert
apple_scep_key: /path/to/scep_key
apple_scep_challenge: scepchallenge
apple_bm_server_token: /path/to/server_token.p7m
apple_bm_cert: /path/to/bm_cert
apple_bm_key: /path/to/private_key
okta_server_url: https://example.okta.com
okta_client_id: 9oa4eoxample2rpdi1087
okta_client_secret: COp8o5zskEQ0OylgjqTrd0xu7rQLx-VteaQW4YGf
eula_url: https://example.com/eula.pdf
Managing osquery configurations
We recommend that you use an infrastructure configuration management tool to manage these osquery configurations consistently across your environment. If you're unsure about what configuration management tools your organization uses, contact your company's system administrators. If you are evaluating new solutions for this problem, the founders of Fleet have successfully managed configurations in large production environments using Chef and Puppet.
Running with systemd
Once you've verified that you can run Fleet in your shell, you'll likely want to keep Fleet running in the background and after the server reboots. To do that we recommend using systemd.
Below is a sample unit file, assuming a fleet user exists on the system. Any user with sufficient
permissions to execute the binary, open the configuration files, and write the log files can be
used. It is also possible to run as root, though as with any other web server it is discouraged
to run Fleet as root.
[Unit]
Description=Fleet
After=network.target
[Service]
User=fleet
Group=fleet
LimitNOFILE=8192
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/fleet serve \
--mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 \
--mysql_database=fleet \
--mysql_username=root \
--mysql_password=toor \
--redis_address=127.0.0.1:6379 \
--server_cert=/tmp/server.cert \
--server_key=/tmp/server.key \
--logging_json
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Once you created the file, you need to move it to /etc/systemd/system/fleet.service and start the service.
sudo mv fleet.service /etc/systemd/system/fleet.service
sudo systemctl start fleet.service
sudo systemctl status fleet.service
sudo journalctl -u fleet.service -f
Making changes
Sometimes you'll need to update the systemd unit file defining the service. To do that, first open /etc/systemd/system/fleet.service in a text editor, and make your modifications.
Then, run
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart fleet.service
Using a proxy
If you are in an enterprise environment where Fleet is behind a proxy and you would like to be able to retrieve Vulnerability data for Vulnerability Processing, it may be necessary to configure the proxy settings. Fleet automatically uses the HTTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY, and NO_PROXY environment variables.
For example, to configure the proxy in a systemd service file:
[Service]
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=http(s)://PROXY_URL:PORT/"
Environment="HTTPS_PROXY=http(s)://PROXY_URL:PORT/"
Environment="NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,::1"
After modifying the configuration you will need to reload and restart the Fleet service, as explained above.
Configuring single sign-on (SSO)
Fleet supports SAML single sign-on capability.
Fleet supports both SP-initiated SAML login and IDP-initiated login. However, IDP-initiated login must be enabled in the web interface's SAML single sign-on options.
Fleet supports the SAML Web Browser SSO Profile using the HTTP Redirect Binding.
Note: The email used in the SAML Assertion must match a user that already exists in Fleet unless you enable JIT provisioning.
Identity provider (IDP) configuration
Setting up the service provider (Fleet) with an identity provider generally requires the following information:
-
Assertion Consumer Service - This is the call-back URL that the identity provider will use to send security assertions to Fleet. In Okta, this field is called single sign-on URL. On Google, it is "ACS URL." The value you supply will be a fully qualified URL consisting of your Fleet web address and the call-back path
/api/v1/fleet/sso/callback. For example, if your Fleet web address is https://fleet.example.com, then the value you would use in the identity provider configuration would be:https://fleet.example.com/api/v1/fleet/sso/callback -
Entity ID - This value is an identifier that you choose. It identifies your Fleet instance as the service provider that issues authorization requests. The value must match the Entity ID that you define in the Fleet SSO configuration.
-
Name ID Format - The value should be
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress. This may be shortened in the IDP setup to something likeemailorEmailAddress. -
Subject Type (Application username in Okta) -
email.
After supplying the above information, the IDP will generate an issuer URI and metadata that will be used to configure Fleet as a service provider.
Fleet SSO configuration
A Fleet user must be assigned the Admin role to configure Fleet for SSO. In Fleet, SSO configuration settings are located in Settings > Organization settings > SAML single sign-on options.
If your IDP supports dynamic configuration, like Okta, you only need to provide an identity provider name and entity ID, then paste a link in the metadata URL field. Make sure you create the SSO application within your IDP before configuring it in Fleet.
Otherwise, the following values are required:
-
Identity provider name - A human-readable name of the IDP. This is rendered on the login page.
-
Entity ID - A URI that identifies your Fleet instance as the issuer of authorization requests (e.g.,
fleet.example.com). This must match the Entity ID configured with the IDP. -
Metadata URL - Obtain this value from the IDP and is used by Fleet to issue authorization requests to the IDP.
-
Metadata - If the IDP does not provide a metadata URL, the metadata must be obtained from the IDP and entered. Note that the metadata URL is preferred if the IDP provides metadata in both forms.
Example Fleet SSO configuration
Creating SSO users in Fleet
When an admin creates a new user in Fleet, they may select the Enable single sign on option. The
SSO-enabled users will not be able to sign in with a regular user ID and password.
It is strongly recommended that at least one admin user is set up to use the traditional password-based login so that there is a fallback method for logging into Fleet in the event of SSO configuration problems.
Individual users must also be set up on the IDP before signing in to Fleet.
Enabling SSO for existing users in Fleet
As an admin, you can enable SSO for existing users in Fleet. To do this, go to the Settings page, then click on the Users tab. Locate the user you want to enable SSO for and on the Actions dropdown menu for that user, click on "Enable single sign-on."
Just-in-time (JIT) user provisioning
Applies only to Fleet Premium
When JIT user provisioning is turned on, Fleet will automatically create an account when a user logs in for the first time with the configured SSO. This removes the need to create individual user accounts for a large organization.
The new account's email and full name are copied from the user data in the SSO response. By default, accounts created via JIT provisioning are assigned the Global Observer role. To assign different roles for accounts created via JIT provisioning see Customization of user roles below.
To enable this option, go to Settings > Organization settings > single sign-on options and check "Automatically create Observer user on login" or adjust your config.
For this to work correctly make sure that:
- Your IDP is configured to send the user email as the Name ID (instructions for configuring different providers are detailed below)
- Your IDP sends the full name of the user as an attribute with any of the following names (if this value is not provided Fleet will fallback to the user email)
namedisplaynamecnurn:oid:2.5.4.3http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name
Customization of user roles
Users created via JIT provisioning can be assigned Fleet roles using SAML custom attributes that are sent by the IdP in SAMLResponses during login.
Fleet will attempt to parse SAML custom attributes with the following format:
FLEET_JIT_USER_ROLE_GLOBAL: Specifies the global role to use when creating the user.FLEET_JIT_USER_ROLE_TEAM_<TEAM_ID>: Specifies team role for team with ID<TEAM_ID>to use when creating the user.
Currently supported values for the above attributes are: admin, maintainer and observer.
SAML supports multi-valued attributes, Fleet will always use the last value.
NOTE: Setting both FLEET_JIT_USER_ROLE_GLOBAL and FLEET_JIT_USER_ROLE_TEAM_<TEAM_ID> will cause an error during login as Fleet users cannot be Global users and belong to teams.
During every SSO login, if sso_settings.enable_jit_role_sync is set to true (default is false) and if the account already exists, the roles of the Fleet account will be updated to match those set in the SAML custom attributes.
IMPORTANT: Beware that if
sso_settings.enable_jit_role_syncis set totruebut no SAML role attributes are configured for accounts then all Fleet users are changed to Global observers on every SSO login (overriding any previous role change).
If none of the attributes above are set, then Fleet will default to use the Global Observer role.
Here's a SAMLResponse sample to set the role of SSO users to Global admin:
[...]
<saml2:Assertion ID="id16311976805446352575023709" IssueInstant="2023-02-27T17:41:53.505Z" Version="2.0" xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<saml2:Issuer Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:entity" xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion">http://www.okta.com/exk8glknbnr9Lpdkl5d7</saml2:Issuer>
[...]
<saml2:Subject xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion">
<saml2:NameID Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress">bar@foo.example.com</saml2:NameID>
<saml2:SubjectConfirmation Method="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:cm:bearer">
<saml2:SubjectConfirmationData InResponseTo="id1Juy6Mx2IHYxLwsi" NotOnOrAfter="2023-02-27T17:46:53.506Z" Recipient="https://foo.example.com/api/v1/fleet/sso/callback"/>
</saml2:SubjectConfirmation>
</saml2:Subject>
[...]
<saml2:AttributeStatement xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion">
<saml2:Attribute Name="FLEET_JIT_USER_ROLE_GLOBAL" NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified">
<saml2:AttributeValue xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">admin</saml2:AttributeValue>
</saml2:Attribute>
</saml2:AttributeStatement>
</saml2:Assertion>
[...]
Here's a SAMLResponse sample to set the role of SSO users to observer in team with ID 1 and maintainer in team with ID 2:
[...]
<saml2:Assertion ID="id16311976805446352575023709" IssueInstant="2023-02-27T17:41:53.505Z" Version="2.0" xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<saml2:Issuer Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:entity" xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion">http://www.okta.com/exk8glknbnr9Lpdkl5d7</saml2:Issuer>
[...]
<saml2:Subject xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion">
<saml2:NameID Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress">bar@foo.example.com</saml2:NameID>
<saml2:SubjectConfirmation Method="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:cm:bearer">
<saml2:SubjectConfirmationData InResponseTo="id1Juy6Mx2IHYxLwsi" NotOnOrAfter="2023-02-27T17:46:53.506Z" Recipient="https://foo.example.com/api/v1/fleet/sso/callback"/>
</saml2:SubjectConfirmation>
</saml2:Subject>
[...]
<saml2:AttributeStatement xmlns:saml2="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion">
<saml2:Attribute Name="FLEET_JIT_USER_ROLE_TEAM_1" NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified">
<saml2:AttributeValue xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">observer</saml2:AttributeValue>
</saml2:Attribute>
<saml2:Attribute Name="FLEET_JIT_USER_ROLE_TEAM_2" NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified">
<saml2:AttributeValue xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">maintainer</saml2:AttributeValue>
</saml2:Attribute>
</saml2:AttributeStatement>
</saml2:Assertion>
[...]
Each IdP will have its own way of setting these SAML custom attributes, here are instructions for how to set it for Okta: https://support.okta.com/help/s/article/How-to-define-and-configure-a-custom-SAML-attribute-statement?language=en_US.
Okta IDP configuration
Once configured, you will need to retrieve the Issuer URI from the View Setup Instructions and metadata URL from the Identity Provider metadata link within the application Sign on settings. See below for where to find them:
The Provider Sign-on URL within the
View Setup Instructionshas a similar format as the Provider SAML Metadata URL, but this link provides a redirect to sign into the application, not the metadata necessary for dynamic configuration.
The names of the items required to configure an identity provider may vary from provider to provider and may not conform to the SAML spec.
Google Workspace IDP Configuration
Follow these steps to configure Fleet SSO with Google Workspace. This will require administrator permissions in Google Workspace.
- Navigate to the Web and Mobile Apps section of the Google Workspace dashboard. Click Add App -> Add custom SAML app.
- Enter
Fleetfor the App name and click Continue.
- Click Download Metadata, saving the metadata to your computer. Click Continue.
- In Fleet, navigate to the Organization Settings page. Configure the SAML single sign-on options section.
- Check the Enable single sign-on checkbox.
- For Identity provider name, use
Google. - For Entity ID, use a unique identifier such as
fleet.example.com. Note that Google seems to error when the provided ID includeshttps://. - For Metadata, paste the contents of the downloaded metadata XML from step three.
- All other fields can be left blank.
Click Update settings at the bottom of the page.
- In Google Workspace, configure the Service provider details.
- For ACS URL, use
https://<your_fleet_url>/api/v1/fleet/sso/callback(e.g.,https://fleet.example.com/api/v1/fleet/sso/callback). - For Entity ID, use the same unique identifier from step four (e.g.,
fleet.example.com). - For Name ID format, choose
EMAIL. - For Name ID, choose
Basic Information > Primary email. - All other fields can be left blank.
Click Continue at the bottom of the page.
- Click Finish.
- Click the down arrow on the User access section of the app details page.
- Check ON for everyone. Click Save.
- Enable SSO for a test user and try logging in. Note that Google sometimes takes a long time to propagate the SSO configuration, and it can help to try logging in to Fleet with an Incognito/Private window in the browser.
Public IPs of devices
IMPORTANT: In order for this feature to work properly, devices must connect to Fleet via the public internet. If the agent connects to Fleet via a private network then the "Public IP address" for such device will not be set.
Fleet attempts to deduce the public IP of devices from well-known HTTP headers received on requests made by the osquery agent.
The HTTP request headers are checked in the following order:
- If
True-Client-IPheader is set, then Fleet will extract its value. - If
X-Real-IPheader is set, then Fleet will extract its value. - If
X-Forwarded-Forheader is set, then Fleet will extract the first comma-separated value. - If none of the above headers are present in the HTTP request then Fleet will attempt to use the remote address of the TCP connection (note that on deployments with ingress proxies the remote address seen by Fleet is the IP of the ingress proxy).
If the IP retrieved using the above heuristic belongs to a private range, then Fleet will ignore it and will not set the "Public IP address" field for the device.