* Update deploying-fleet-on-aws-with-terraform.md Changed title to be consistent with other deployment guides. * Update deploying-fleet-on-render.md Changed title to be consistent with other deployment guides. * Update deploy-fleet-on-hetzner-cloud.md Changed title to remove the ampersand and make "Cloud-init" lowercase.
22 KiB
Deploy Fleet on Hetzner Cloud with cloud-init and Docker
Hetzner is a great price-performance provider for “root” (dedicated) and Virtual Private Servers (VPS) with high performance and generous bandwidth.
While other providers may charge large amounts for computing and storage, Hetzner is cost-effective and scalable, with great managed options (such as Nextcloud).
Let’s explore how you might deploy Fleet on Hetzner Cloud as quickly as possible so you can use Fleet to orchestrate osquery on your endpoints.
The 2 minute setup
For those who want to get started quickly, copy and paste the following two scripts into cloud-init User-Data. Alternatively, the more adventurous can follow the full deployment guide.
Fleet
Copy and paste the following script into cloud-init User-Data for the Fleet controller machine, replacing FLEET_DOMAIN with your Fleet machine TLD:
#!/usr/bin/bash
# DONT FORGET: Replace the line below with your fleet machine TLD
export FLEET_DOMAIN=fleet.domain.tld
#######
# DNS #
#######
# Set up DNS resolution
sed -i /etc/systemd/resolved.conf 's/^#DNS=$/DNS=1.1.1.1 9.9.9.9 8.8.8.8/'
systemctl restart systemd-resolved
#######
# APT #
#######
# Update Apt
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
############
# Firewall #
############
apt install ufw
ufw deny all
ufw allow ssh
ufw allow http
ufw allow https
ufw enable
############
# Fail2Ban #
############
apt install fail2ban
##########
# Docker #
##########
apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release # these should already be installed
# Set up package repositories for docker
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
# Install docker
apt update
apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
docker pull mysql@sha256:16e159331007eccc069822f7b731272043ed572a79a196a05ffa2ea127caaf67 # mysql:5.7.38 as of 2022/05/19
######################
# MySQL (dockerized) #
######################
# mysql:5.7.38 as of 2022/05/19
docker pull mysql@sha256:16e159331007eccc069822f7b731272043ed572a79a196a05ffa2ea127caaf67
# Create the Fleet MySQL data folder
mkdir -p /etc/fleet
# Create ENV that will be used by the docker container
touch /etc/fleet/mysql.env
chmod 600 /etc/fleet/mysql.env
echo "MYSQL_HOST=127.0.0.1" >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
echo "MYSQL_USER=fleet" >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
echo "MYSQL_DATABASE=fleet" >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1 | sed -e 's/^/MYSQL_PASSWORD=/' >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1 | sed -e 's/^/MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=/' >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
cat <<EOF > /etc/systemd/system/fleet-mysql.service
[Unit]
Description=Fleet MySQL instance
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull mysql@sha256:16e159331007eccc069822f7b731272043ed572a79a196a05ffa2ea127caaf67
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
-p 127.0.0.1:3306:3306 \
-v /etc/fleet/mysql:/var/lib/mysql \
--env-file /etc/fleet/mysql.env \
mysql@sha256:16e159331007eccc069822f7b731272043ed572a79a196a05ffa2ea127caaf67
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop %n
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable fleet-mysql
systemctl start fleet-mysql
######################
# Redis (Dockerized) #
######################
docker pull eqalpha/keydb@sha256:18a00f69577105650d829ef44a9716eb4feaa7a5a2bfacd115f0a1e7a97a8726
cat <<EOF > /etc/systemd/system/fleet-redis.service
[Unit]
Description=Fleet Redis instance
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
# eqalpha/keydb:x86_64_v6.3.0 as of 2022-05-19
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull eqalpha/keydb@sha256:18a00f69577105650d829ef44a9716eb4feaa7a5a2bfacd115f0a1e7a97a8726
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
-p 127.0.0.1:6379:6379 \
-v /etc/fleet/redis:/var/lib/redis \
eqalpha/keydb@sha256:18a00f69577105650d829ef44a9716eb4feaa7a5a2bfacd115f0a1e7a97a8726
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop %n
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable fleet-redis
systemctl start fleet-redis
######################
# Fleet (Dockerized) #
######################
docker pull fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b
mkdir -p /etc/fleet/fleet
# MySQL fleet ENV
bash -c 'source /etc/fleet/mysql.env && echo -e "FLEET_MYSQL_USERNAME=$MYSQL_USER" >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env';
bash -c 'source /etc/fleet/mysql.env && echo -e "FLEET_MYSQL_PASSWORD=$MYSQL_PASSWORD" >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env';
echo 'FLEET_MYSQL_DATABASE=fleet' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
# Other fleet ENV vars
echo 'FLEET_SERVER_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:8080' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
echo 'FLEET_MYSQL_ADDRESS=localhost:3306' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
echo 'FLEET_REDIS_ADDRESS=localhost:6379' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
echo 'FLEET_SERVER_TLS=false' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
cat <<EOF > /etc/systemd/system/fleet.service
[Unit]
Description=Fleet
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b
ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name fleet-prepare-db \
--net=host \
--env-file=/etc/fleet/fleet.env \
fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b \
/usr/bin/fleet prepare db --no-prompt --logging_debug
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
--net=host \
-p 127.0.0.1:8080:8080 \
--env-file=/etc/fleet/fleet.env \
fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b \
/usr/bin/fleet serve
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable fleet
systemctl start fleet
######################
# Caddy (Dockerized) #
######################
mkdir -p /etc/fleet/caddy;
touch /etc/fleet/caddy.env;
chmod 600 /etc/fleet/caddy.env;
echo -e "FLEET_DOMAIN=${FLEET_DOMAIN}" >> /etc/fleet/caddy.env; # Replace this with your domain!
cat <<EOF > /etc/fleet/caddy/Caddyfile
{\$FLEET_DOMAIN}
reverse_proxy 127.0.0.1:8080
EOF
docker pull caddy@sha256:6e62b63d4d7a4826f9e93c904a0e5b886a8bea2234b6569e300924282a2e8e6c
cat <<EOF > /etc/systemd/system/fleet-caddy.service
[Unit]
Description=Fleet Caddy instance
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
EnvironmentFile=/etc/fleet/caddy.env
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
# caddy:2.5.1-alpine as of 2022-05-20
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull caddy@sha256:6e62b63d4d7a4826f9e93c904a0e5b886a8bea2234b6569e300924282a2e8e6c
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
--env-file=/etc/fleet/caddy.env \
--net=host \
-v /etc/fleet/caddy/Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile \
-v /etc/fleet/caddy/data:/data \
-v /etc/fleet/caddy/config:/config \
caddy@sha256:6e62b63d4d7a4826f9e93c904a0e5b886a8bea2234b6569e300924282a2e8e6c
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable fleet-caddy
systemctl start fleet-caddy
Host
Copy and paste the script below into cloud-init User-Data for your hosts (which run osqueryd and workloads).
The Fleet version number in the script can be swapped for the latest.
#!/usr/bin/bash
#######
# DNS #
#######
# Set up DNS resolution
sed -i /etc/systemd/resolved.conf 's/^#DNS=$/DNS=1.1.1.1 9.9.9.9 8.8.8.8/'
systemctl restart systemd-resolved
#######
# APT #
#######
# Update Apt
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
############
# Firewall #
############
apt install ufw
ufw deny all
ufw allow ssh
ufw allow http
ufw allow https
ufw enable
############
# Fail2Ban #
############
apt install fail2ban
############
# fleetctl #
############
wget https://github.com/fleetdm/fleet/releases/download/fleet-v4.15.0/fleetctl_v4.15.0_linux.tar.gz
echo "cd50f058724cdde07edcc3cf89c83e9c5cd91ca41974ea470ae660cb50dd04a1 fleetctl_v4.15.0_linux.tar.gz" | sha256sum -c
tar --extract --file=fleetctl_v4.15.0_linux.tar.gz fleetctl_v4.15.0_linux/fleetctl
mv fleetctl_v4.15.0_linux/fleetctl /usr/bin/fleetctl
##########################
# Machine Workload Setup #
##########################
### Your normal node setup goes here
### (after the Fleet instance is running, you'll get a command like the one below to run on hosts)
### $ fleetctl package --type=deb --fleet-url=https://fleet.vadosware.io --enroll-secret=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
### (Running the command above produces a .DEB package you can install like the example below)
### $ apt install /root/fleet-osquery_0.0.13_amd64.deb
### (After this, you should be able to see your new machine on the fleet instance! 🎉)
The full deployment guide
For the more adventurous, here are the complete instructions for deploying Fleet on Hetzner with cloud-init and Docker from scratch.
Prerequisites
To follow this guide, you’ll need:
- An account with Hetzner
- A practical understanding of Cloud-init, the multi-distribution method for cross platform cloud instance initialization.
- A practical understanding of cloud-init User-Data
- A practical understanding of Docker (or any other container runtime of your choice)
Get a machine from Hetzner
First, purchase a machine (for example, a Hetzner Cloud instance):
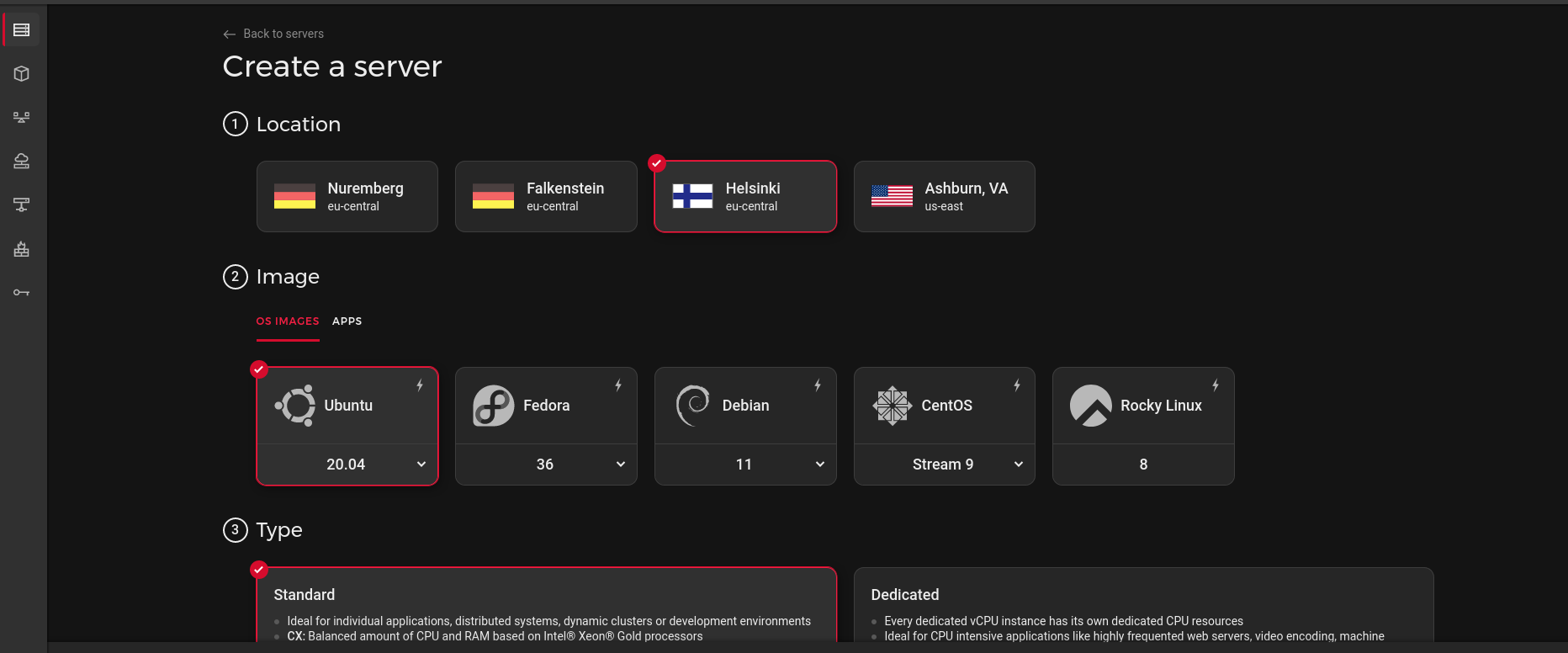 Hetzner cloud purchase machine screen
Hetzner cloud purchase machine screen
After purchasing, you should know the IP address of your machine (and make sure you set up things like SSH securely!)
DNS
For your domain
This would be a great time to set up A/AAAA records for your Fleet controller instance – something like fleet.domain.tld should work (ex. fleet.yoursite.com).
On the machine
Now that we have our machine, we’ll want to allow DNS queries to DNS resolvers other than Hetzner:
sed -i /etc/systemd/resolved.conf 's/^#DNS=$/DNS=1.1.1.1 9.9.9.9 8.8.8.8/'
systemctl restart systemd-resolved
This will ensure that external DNS can be reached through a means other than by Hetzner default DNS nameservers.
Set up APT
Let’s get our machine up to date and install some packages we’ll need later
# Update Apt
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
Set up a firewall
To ensure we do not expose services accidentally, we'll install UncomplicatedFirewall, also known as ufw, to block all inbound traffic by default and then allow the protocols we need.
apt install ufw
ufw deny all
ufw allow ssh
ufw allow http
ufw allow https
ufw enable
Docker
Before we can get started, let’s install Docker to manage our workloads. Other container runtimes would work, but Docker is pretty well known, robust, and uses Containerd underneath anyway, so let’s use that:
sudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release # these should already be installed
# Set up package repositories for docker
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
$ echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
# Install docker
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
NOTE: This is a UserData script, so we don’t have to worry about removing previous existing versions! See the official Docker Ubuntu install documentation for more details.
MySQL
Fleet uses MySQL as its primary data store, so first, we’ll have to set up MySQL.
To run MySQL, we’ll have to do the following:
Pull the MySQL container
We can pull the official MySQL docker image like so:
$ docker pull mysql@sha256:16e159331007eccc069822f7b731272043ed572a79a196a05ffa2ea127caaf67 # mysql:5.7.38 as of 2022/05/19
Create & enable a systemd unit for MySQL
systemd has become the defacto systems manager for most distros, and as such, we’ll be setting up a systemd unit to ensure MySQL is started automatically.
First we’ll set up our credentials:
# Create the Fleet MySQL data folder
mkdir -p /etc/fleet
# Create ENV that will be used by the docker container
touch /etc/fleet/mysql.env
chmod 600 /etc/fleet/mysql.env
echo "MYSQL_HOST=127.0.0.1" >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
echo "MYSQL_USER=fleet" >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
echo "MYSQL_DATABASE=fleet" >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1 | sed -e 's/^/MYSQL_PASSWORD=/' >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 32 | head -n 1 | sed -e 's/^/MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=/' >> /etc/fleet/mysql.env
And then we’ll create the actual unit that reads this config
[Unit]
Description=Fleet MySQL instance
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull mysql@sha256:16e159331007eccc069822f7b731272043ed572a79a196a05ffa2ea127caaf67
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
-p 127.0.0.1:3306:3306 \
-v /etc/fleet/mysql:/var/lib/mysql \
--env-file /etc/fleet/mysql.env \
mysql@sha256:16e159331007eccc069822f7b731272043ed572a79a196a05ffa2ea127caaf67
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop %n
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
We’ll save this content to /etc/systemd/system/fleet-mysql.service, and refresh systemd:
$ systemctl daemon-reload
$ systemctl enable fleet-mysql
Redis
Fleet uses Redis as its primary caching solution, so we’ll need to set up Redis as well. While “vanilla” Redis is a great choice, a recent entrant to the space is KeyDB, an alternative multi-threaded implementation of Redis.
Pull the Redis KeyDB Docker container
We can pull the KeyDB docker image like so:
$ docker pull eqalpha/keydb@sha256:18a00f69577105650d829ef44a9716eb4feaa7a5a2bfacd115f0a1e7a97a8726 # x86_64_v6.3.0 as of 2022/05/19
Create and enable a Redis systemd service
Similarly to MySQL, a systemd service can be created for our redis-equivalent service as well.
[Unit]
Description=Fleet Redis instance
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull eqalpha/keydb@sha256:18a00f69577105650d829ef44a9716eb4feaa7a5a2bfacd115f0a1e7a97a8726 # eqalpha/keydb:x86_64_v6.3.0 as of 2022-05-19
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
-p 127.0.0.1:6379:6379 \
-v /etc/fleet/redis:/var/lib/redis \
eqalpha/keydb@sha256:18a00f69577105650d829ef44a9716eb4feaa7a5a2bfacd115f0a1e7a97a8726
ExecStop=/usr/bin/docker stop %n
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
We’ll save this content to /etc/systemd/system/fleet-redis.service. And just like MySQL we’ll daemon-reload and enable:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable fleet-redis
Fleet
We’re finally at the main course – time to install Fleet!
Pull the Fleet docker container
We can pull the Fleet docker image like so:
$ docker pull fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b
The Fleet v4.15.0 release can be found in DockerHub.
Create and enable the Fleet systemd service
First, we’ll get our Fleet ENV vars in place:
mkdir -p /etc/fleet/fleet
# MySQL fleet ENV
bash -c 'source /etc/fleet/mysql.env && echo -e "FLEET_MYSQL_USERNAME=$MYSQL_USER" >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env';
bash -c 'source /etc/fleet/mysql.env && echo -e "FLEET_MYSQL_PASSWORD=$MYSQL_PASSWORD" >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env';
echo 'FLEET_MYSQL_DATABASE=fleet' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
# Other fleet ENV vars
echo 'FLEET_SERVER_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:8080' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
echo 'FLEET_MYSQL_ADDRESS=localhost:3306' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
echo 'FLEET_REDIS_ADDRESS=localhost:6379' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
echo 'FLEET_SERVER_TLS=false' >> /etc/fleet/fleet.env
We can set up Fleet to run like so:
[Unit]
Description=Fleet
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b
ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name fleet-prepare-db \
--net=host \
--env-file=/etc/fleet/fleet.env \
fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b \
/usr/bin/fleet prepare db --no-prompt --logging_debug
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
--net=host \
--env-file=/etc/fleet/fleet.env \
fleetdm/fleet@sha256:332744f3503dc15fdb65c7b672a09349b2c30fb59a08f9ab4b1bbab94e3ddb5b \
/usr/bin/fleet serve
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
(Optional) Caddy for automatic HTTPS
To have access to your Fleet instance from far away, we’ll set up a TLS-terminating load balancer like Caddy to do the heavy lifting for us.
Luckily, Caddy supports automatic HTTPS certificate retrieval via LetsEncrypt, so it will make things easier.
First, let’s write our domain as a configuration that systemd can use at /etc/fleet/caddy.env:
mkdir -p /etc/fleet/caddy;
touch /etc/fleet/caddy.env;
chmod 600 /etc/fleet/caddy.env;
echo "FLEET_DOMAIN=fleet.domain.tld" >> /etc/fleet/caddy.env; # Replace this with your domain!
Assuming you have a domain like fleet.domain.tld already purchased and set up; we can get external-reachability for our cluster with Caddy by first writing a Caddyfile:
{$FLEET_DOMAIN}
reverse_proxy 127.0.0.1:8080
After saving that simple Caddyfile at /etc/fleet/caddy/Caddyfile, we can do our usual docker pulling:
$ docker pull caddy@sha256:6e62b63d4d7a4826f9e93c904a0e5b886a8bea2234b6569e300924282a2e8e6c
Here’s a systemd service:
[Unit]
Description=Fleet Caddy instance
After=docker.service
Requires=docker.service
[Service]
TimeoutStartSec=0
Restart=always
EnvironmentFile=/etc/fleet/caddy.env
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker exec %n stop
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker rm %n
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/docker pull caddysha@256:6e62b63d4d7a4826f9e93c904a0e5b886a8bea2234b6569e300924282a2e8e6c # caddy:2.5.1-alpine as of 2022-05-20
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker run --rm \
--name %n \
--env-file=/etc/fleet/caddy.env \
-p 80:80 \
-p 443:443 \
-v /etc/fleet/caddy/Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile \
-v /etc/fleet/caddy/data:/data \
-v /etc/fleet/caddy/config:/config \
caddy@sha256:6e62b63d4d7a4826f9e93c904a0e5b886a8bea2234b6569e300924282a2e8e6c
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
NOTE: if you choose not to use Caddy, you’ll have to generate self-signed certs or use another method.
At this point you should be able to go to your domain (ex. https://fleet.domain.tld) and access Fleet 🎉!
How long does it take?
The User Data script takes around 100 seconds to run: \
Cloud-init v. 22.1-14-g2e17a0d6-0ubuntu1~20.04.3 running 'modules:final' at Thu, 02 Jun 2022 07:22:35 +0000. Up 12.99 seconds.
Cloud-init v. 22.1-14-g2e17a0d6-0ubuntu1~20.04.3 finished at Thu, 02 Jun 2022 07:23:58 +0000. Datasource DataSourceHetzner. Up 94.87 seconds
Set up Fleet and enroll hosts
Now that Fleet is running, visit your Fleet dashboard (i.e., https://fleet.domain.tld) and enter your name, email and password. You should now see the empty hosts page. To start enrolling hosts into Fleet, check out Adding hosts.
What's next?
Now that you’re ready to use Fleet and have a host installed. Here's some next steps:
- Take some time to get acclimatized to Fleet. Learn how to use Fleet and Fleet UI are both great places to start.
- Import Fleet's standard query library to start asking questions about your hosts.
- To run a more secure setup, consider creating a dedicated
fleetuser with Docker's support for user namespaces.
