In this guide, we're going to install Fleet and all of its application dependencies on a CentOS 7.1 server. Once we have Fleet up and running, we're going to install osquery on that same CentOS 7.1 host and enroll it in Fleet. This should give you a good understanding of both how to install Fleet as well as how to install and configure osquery such that it can communicate with Fleet.
### Setting up a host
If you don't have a CentOS host readily available, Fleet recommends using [Vagrant](https://www.vagrantup.com/) for this guide. You can find installation instructions on Vagrant's [downloads page](https://developer.hashicorp.com/vagrant/downloads).
Once you have installed Vagrant, run the following to create a Vagrant box, start it, and log into it:
To install Fleet, [download](https://github.com/fleetdm/fleet/releases) the latest release from GitHub. The binary is in an archive that uses this naming convention, including the current version: `fleet_<version>_linux.tar.gz`.
It's also worth creating a MySQL database for us to use at this point. Run the following to create the `fleet` database in MySQL. Note that you will be prompted for the password you created above.
Now that we have installed Fleet, MySQL, and Redis, we are ready to launch Fleet! First, we must "prepare" the database. We do this via `fleet prepare db`:
Before we can run the server, we need to generate some TLS keying material. If you already have tooling for generating valid TLS certificates, then you are encouraged to use that instead. You will need a TLS certificate and key for running the Fleet server. If you'd like to generate self-signed certificates, you can do this via (replace SERVER_NAME with your server FQDN):
Now, if you go to [https://localhost:8080](https://localhost:8080) in your local browser, you should be redirected to [https://localhost:8080/setup](https://localhost:8080/setup) where you can create your first Fleet user account.
### Running Fleet with systemd
See [Running with systemd](https://fleetdm.com/docs/deploying/configuration#running-with-systemd) for documentation on running fleet as a background process and managing the fleet server logs.
### Installing and running osquery
> Note that this whole process is outlined in more detail in the [Adding Hosts To Fleet](https://fleetdm.com/docs/using-fleet/adding-hosts) document. The steps are repeated here for the sake of a continuous tutorial.
To install osquery on CentOS, you can run the following:
You will need to set the osquery enroll secret and osquery server certificate. If you head over to the manage hosts page on your Fleet instance (which should be [https://localhost:8080/hosts/manage](https://localhost:8080/hosts/manage)), you should be able to click "Add New Hosts" and see a modal like the following:
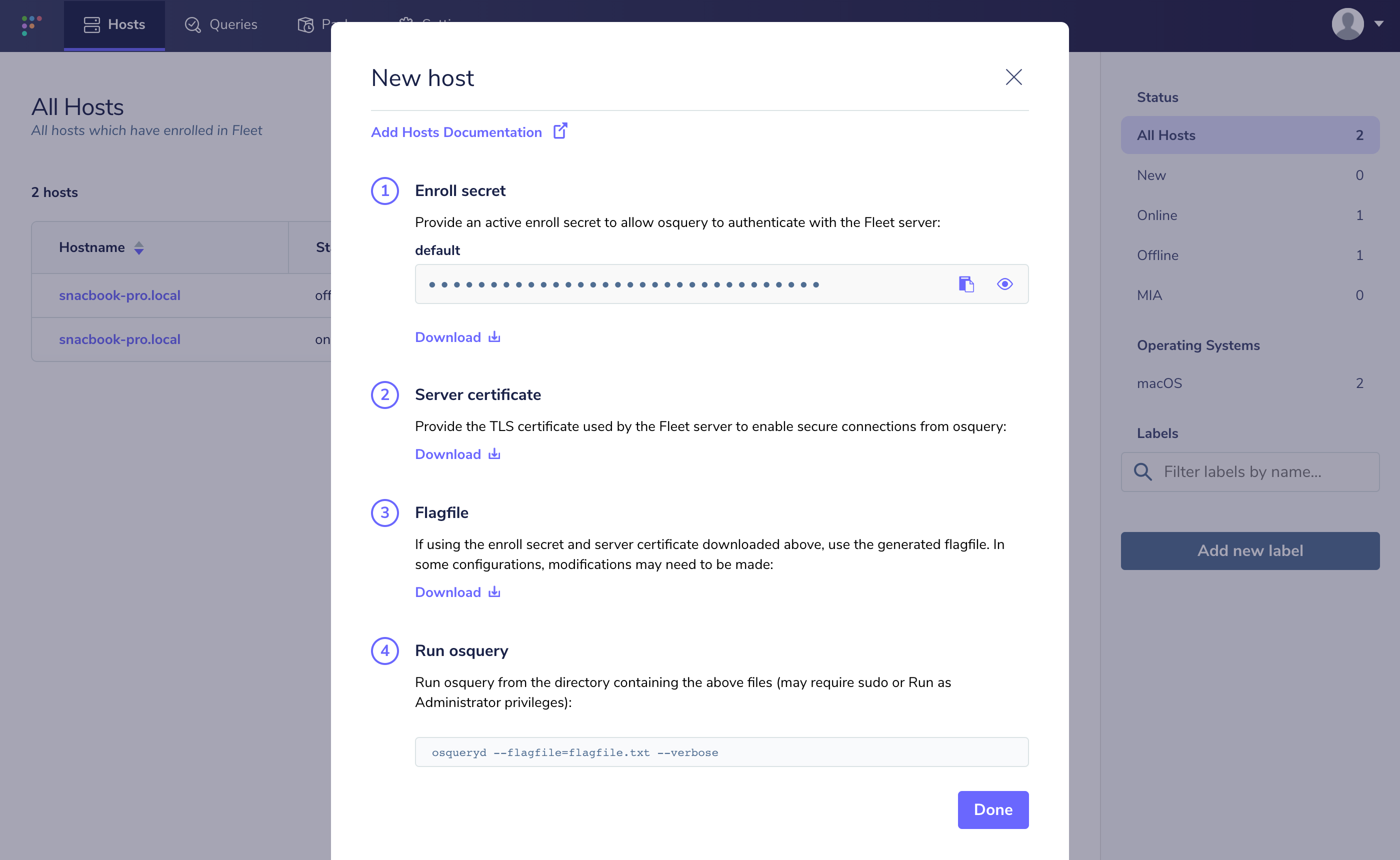
If you select "Fetch Fleet Certificate", your browser will download the appropriate file to your downloads directory (to a file probably called `localhost-8080.pem`). Copy this file to your CentOS host at `/var/osquery/server.pem`.
You can also select "Reveal Secret" on that modal and the enrollment secret for your Fleet instance will be revealed. Copy that text and create a file with its contents: